Publication
† denotes group members under direct supervision * denotes corresponding
2026
|
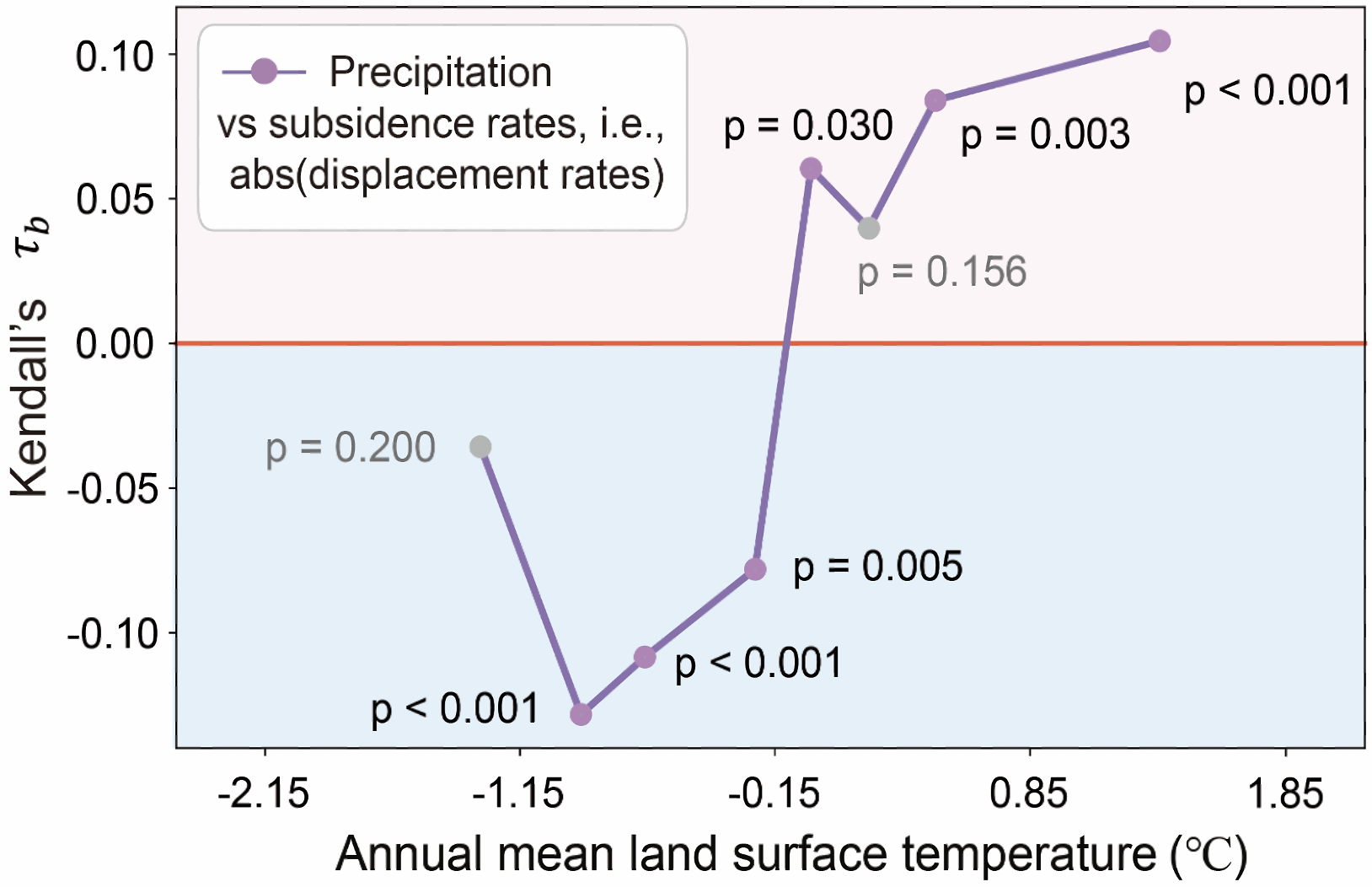
53. Decoupling hydroclimatic controls on displacement of retrogressive thaw slumps in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
|
2025
|
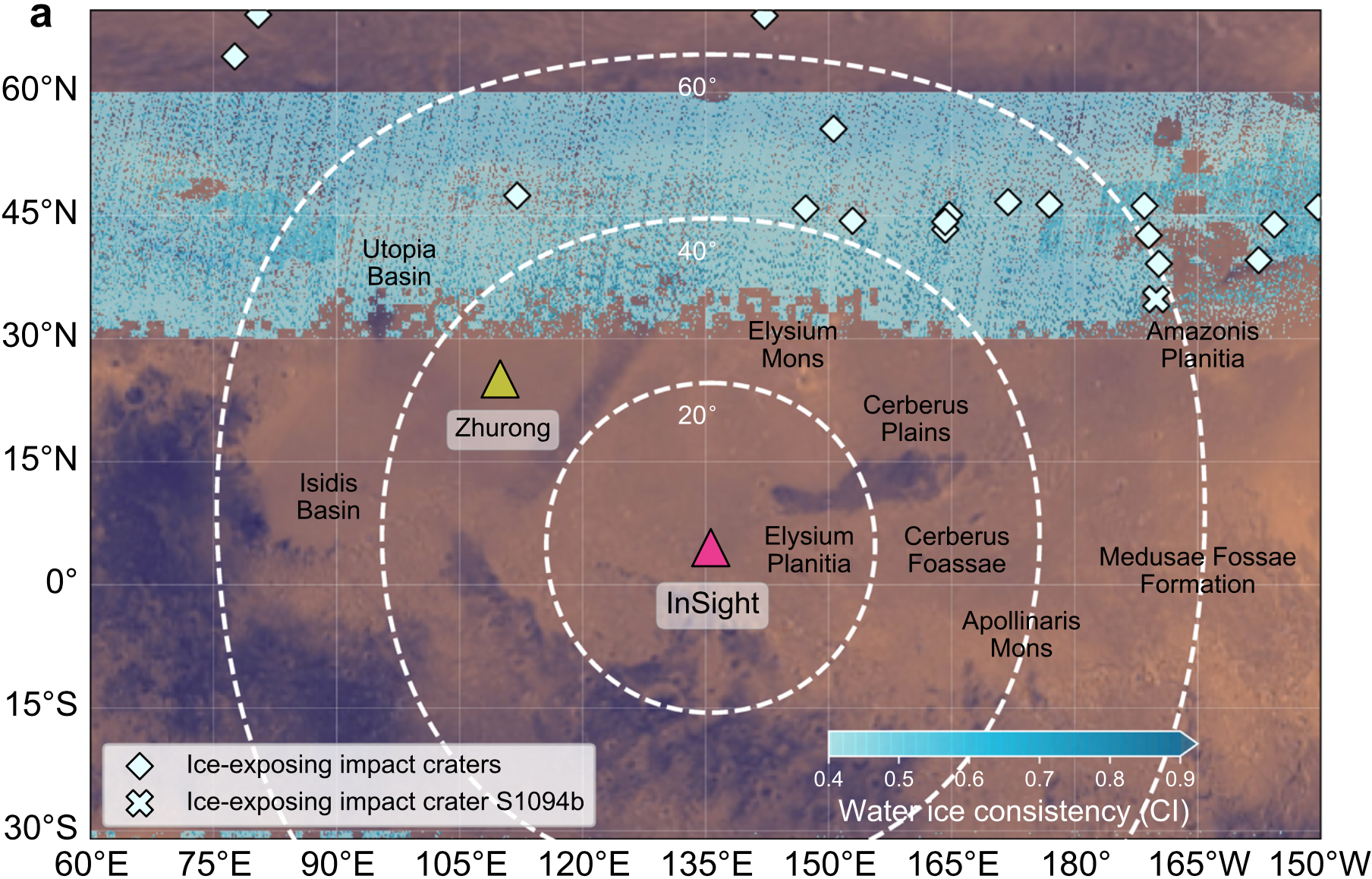
52. Near-Surface liquid water on Mars inferred from seasonal marsquake
|
|
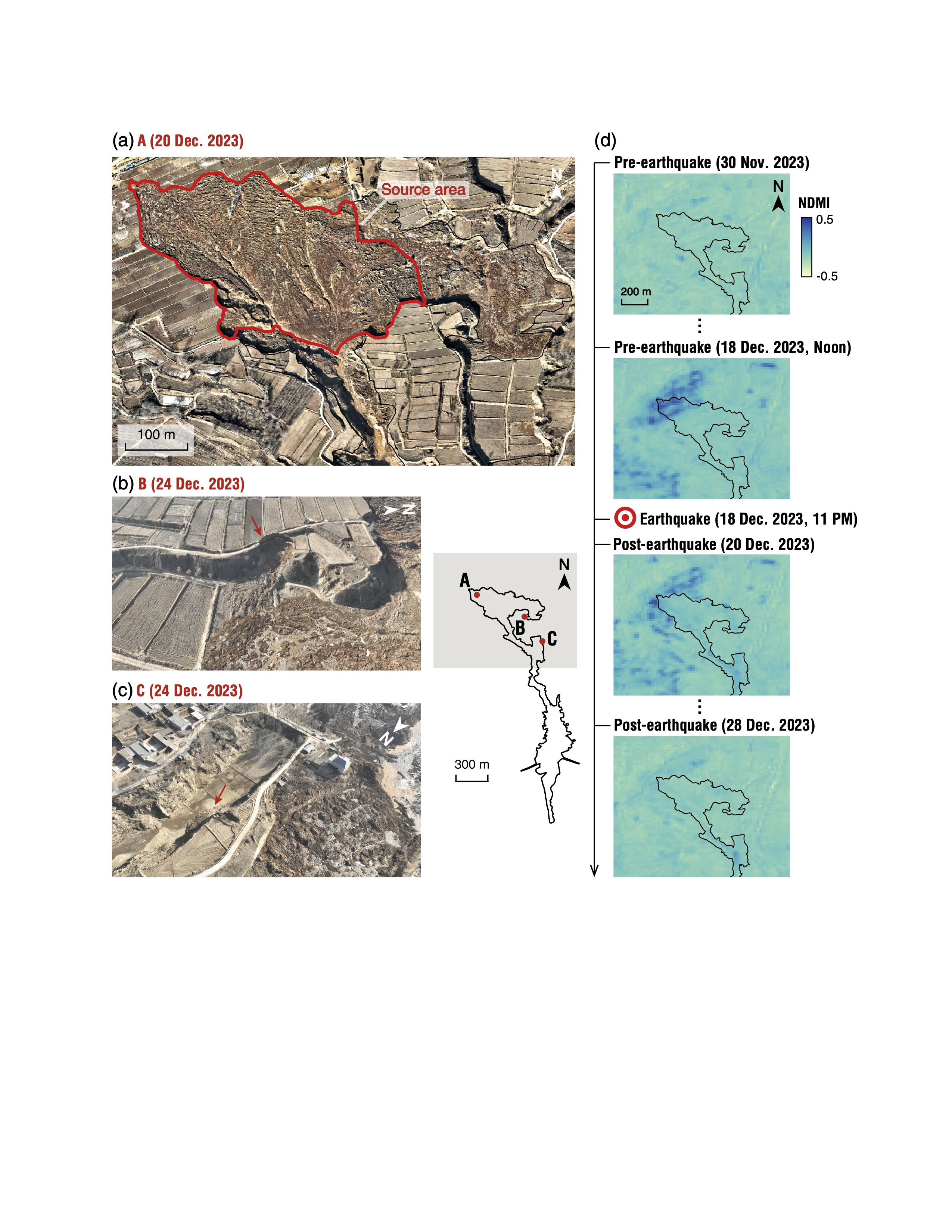
51. Co-seismic landslides and a massive lateral spread of the 2023 Jishishan earthquake in China characterized by intelligent remote sensing analysis
|
|
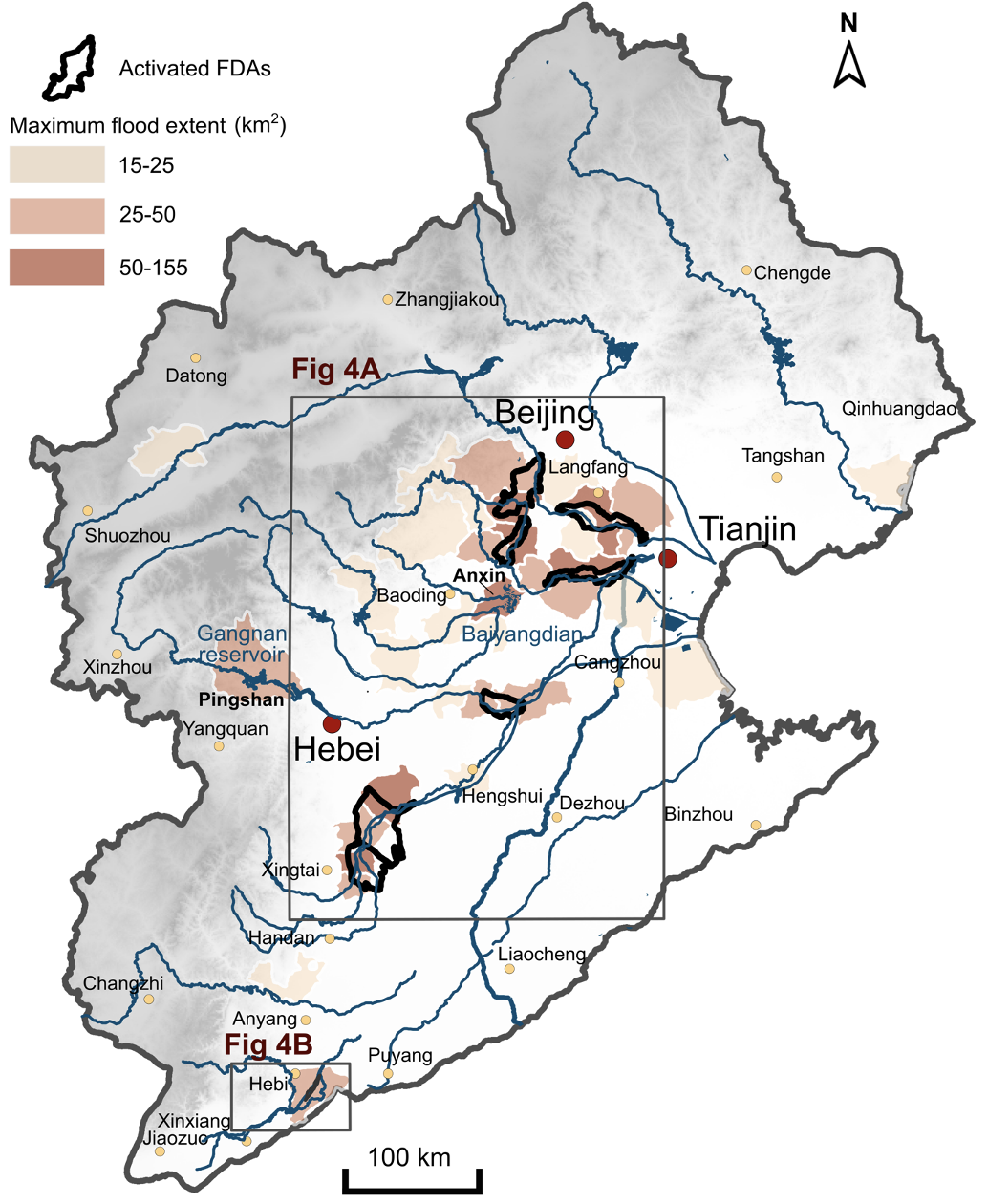
50. Quantifying the lifespan of 3D flood structures: unlocking the potential of flood detention areas for enhanced flood control in China
|
|
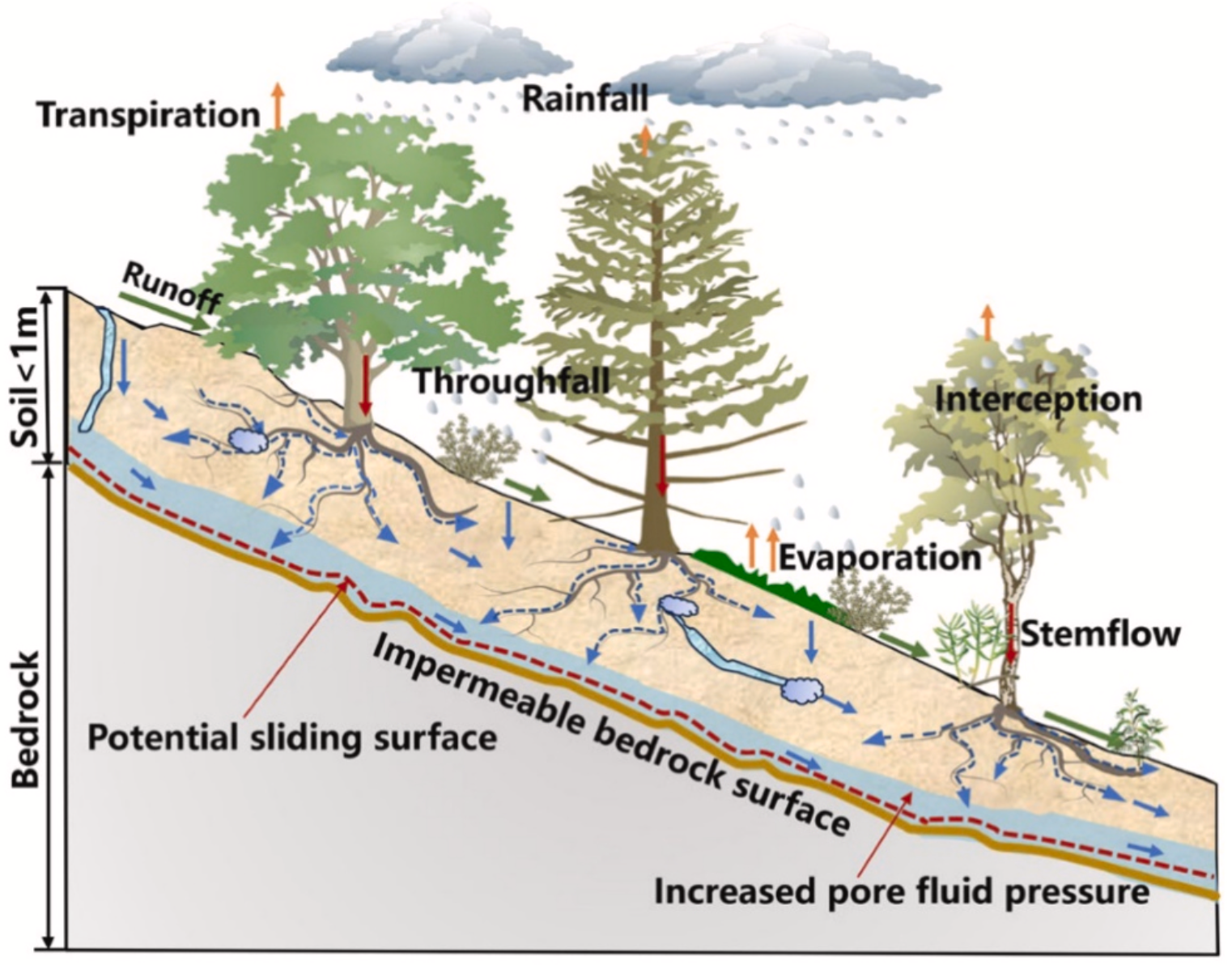
49. Comparing landslide patterns and failure mechanisms in restored and native forest ecosystems: Insights from geomorphology, lithology and vegetation
|
|
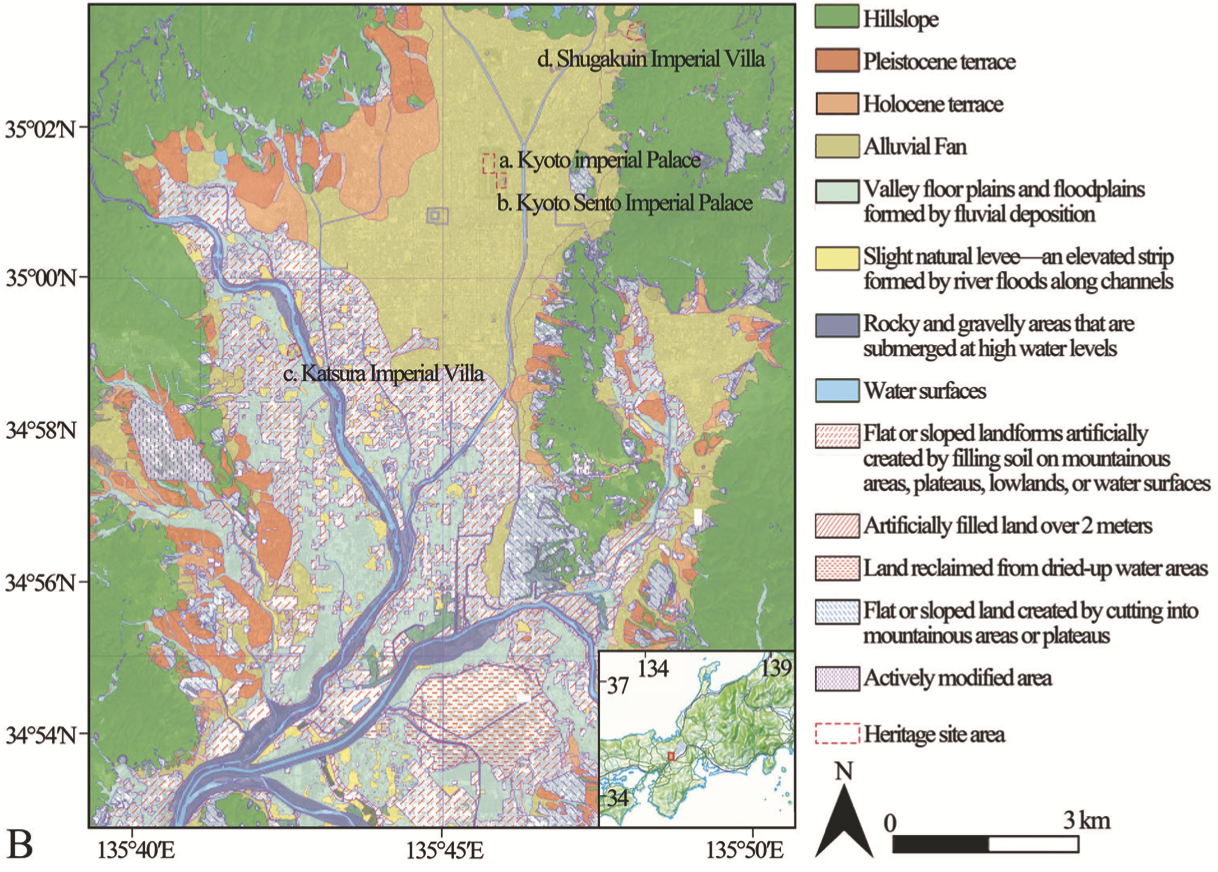
48. Investigating subsidence characteristics of Kyoto Imperial Garden cultural heritage shaped by historical landscape construction, through remote sensing
|
|
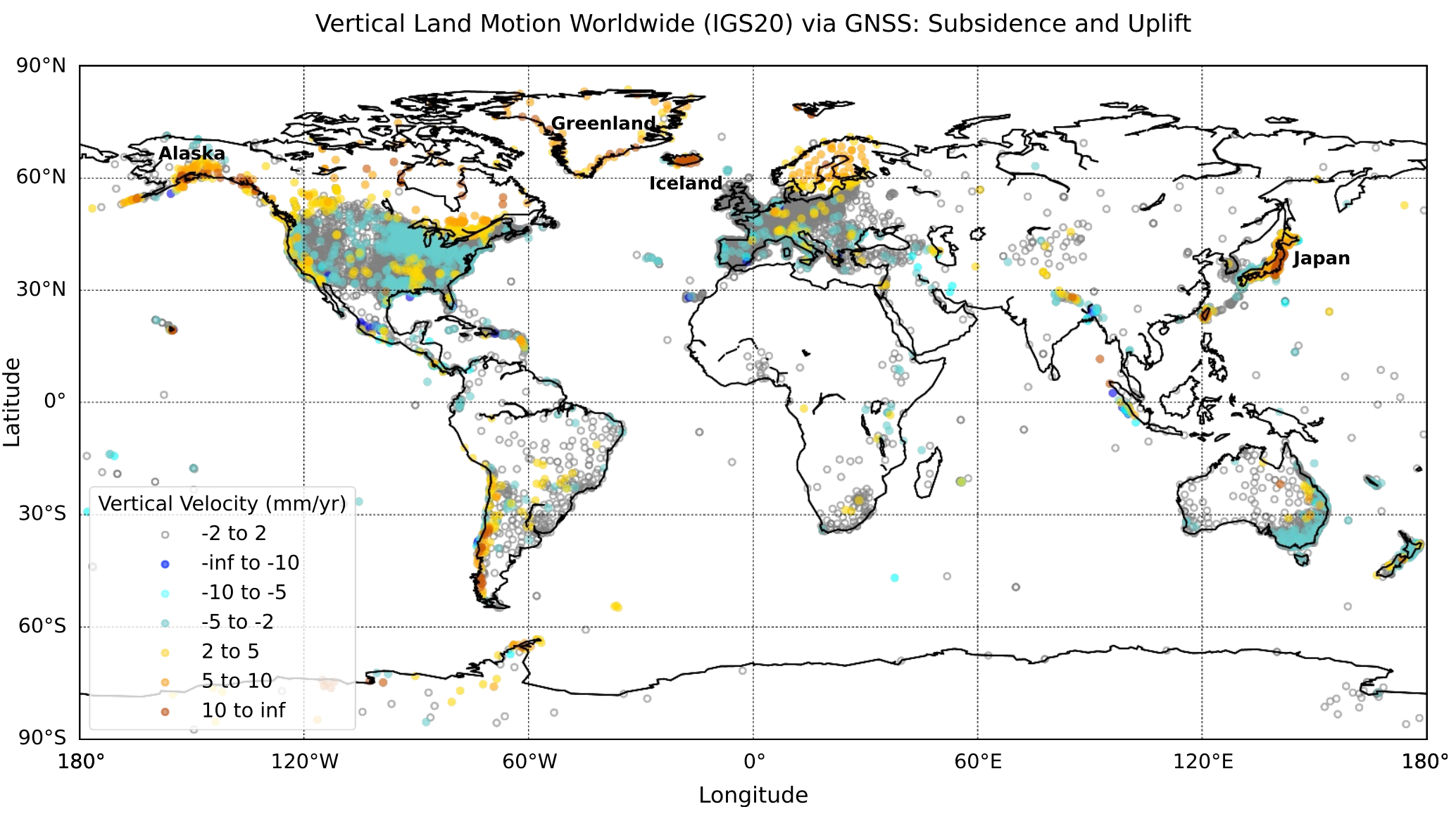
47. ChangePointCNN-GNSS: an AI model for assessing change points and optimizing site velocity estimation from global GNSS data
|
|
46. Kinematic glacier thickness inversion using 3D flow velocities from multi-track SAR images
|
|
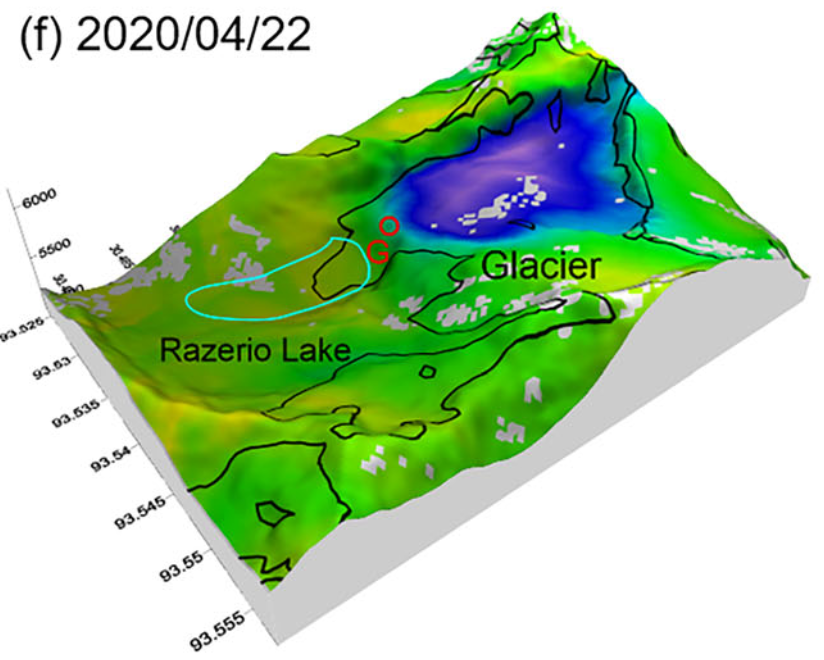
45. Triggering factors and flooding processes of glacial lake outburst flood at Ranzerio lake
|
|
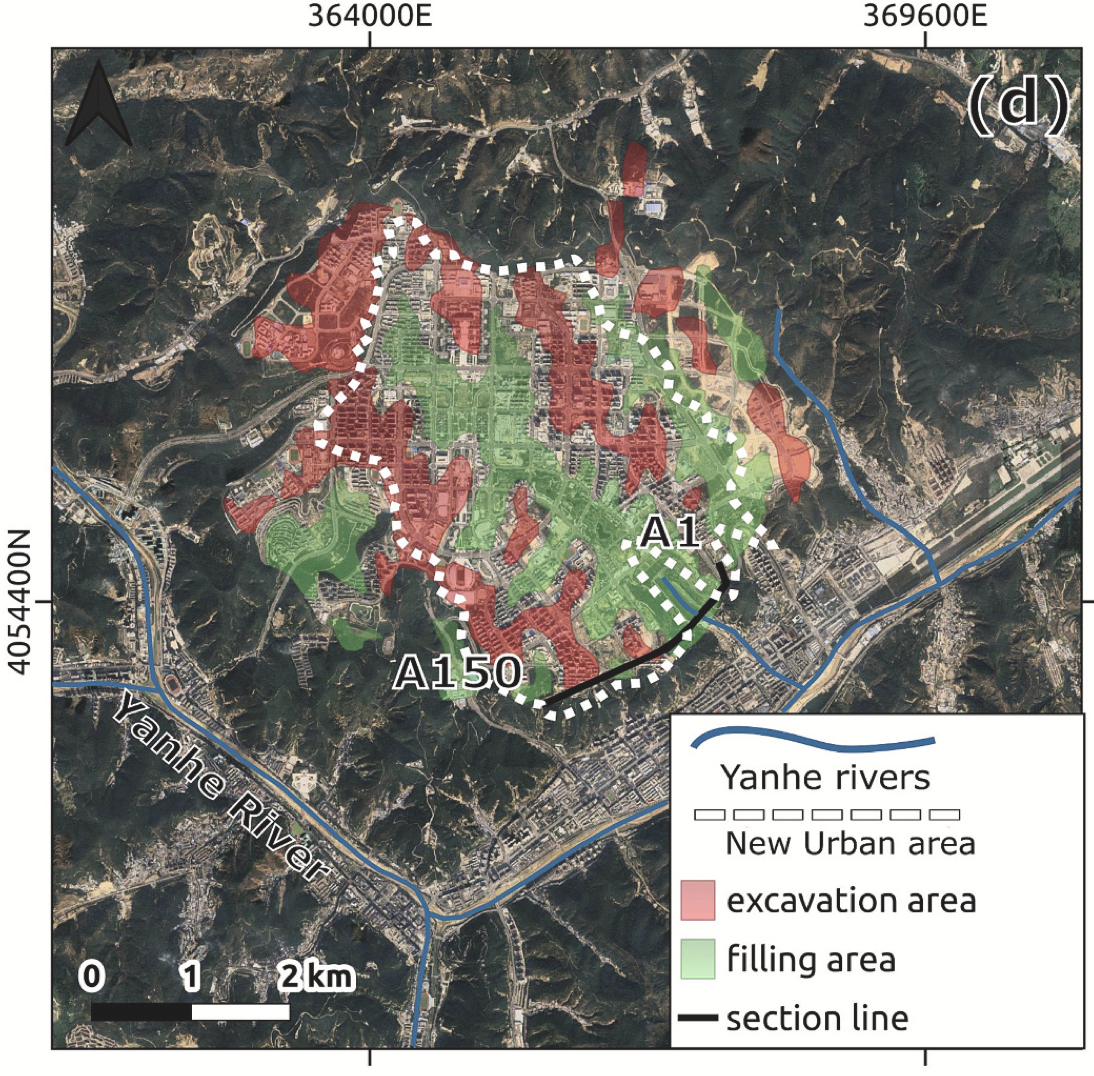
44. Post-anthropogenic landscape evolution: Terrain reshaping and geomorphic response in the Loess Plateau
|
|
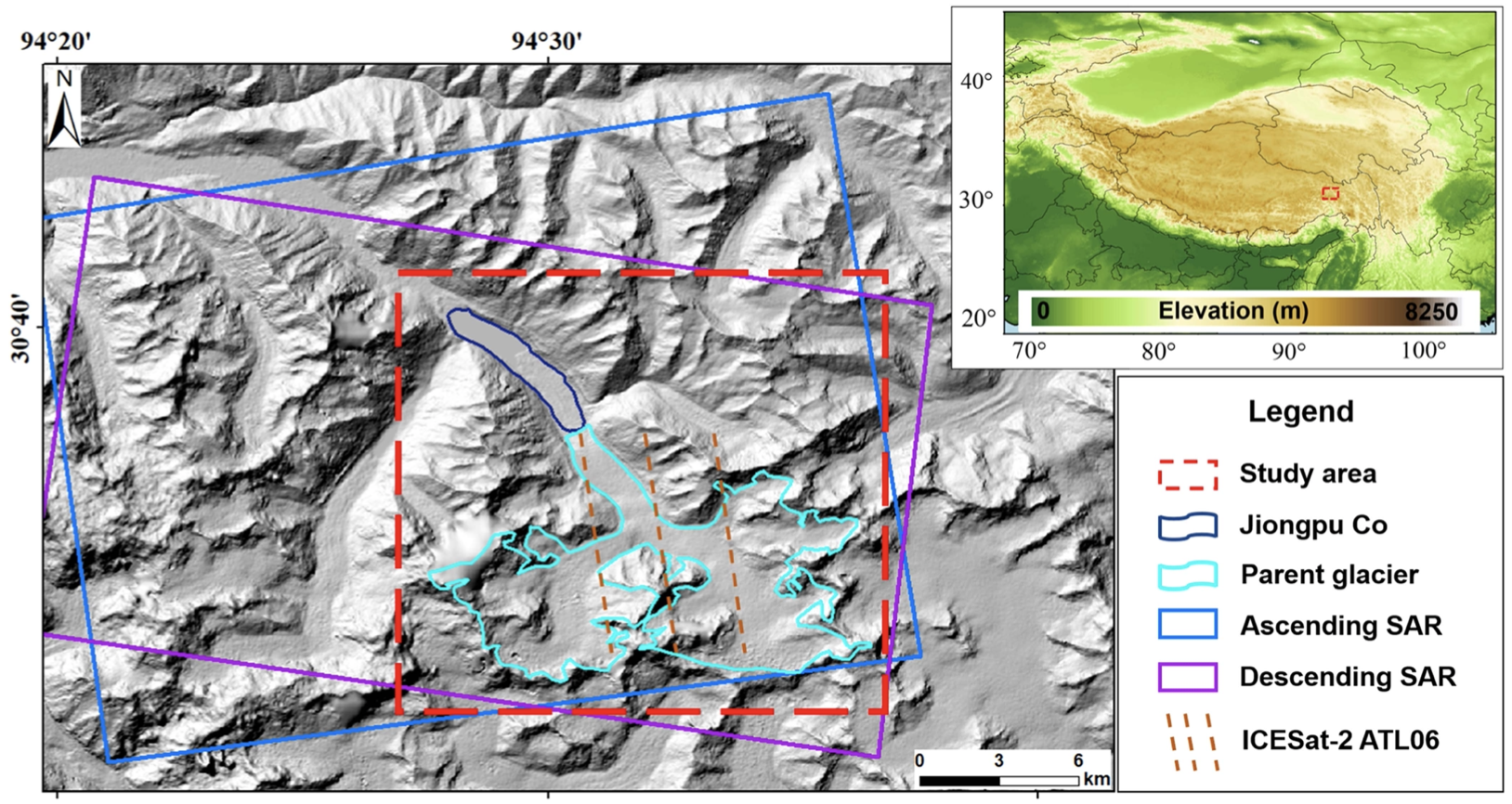
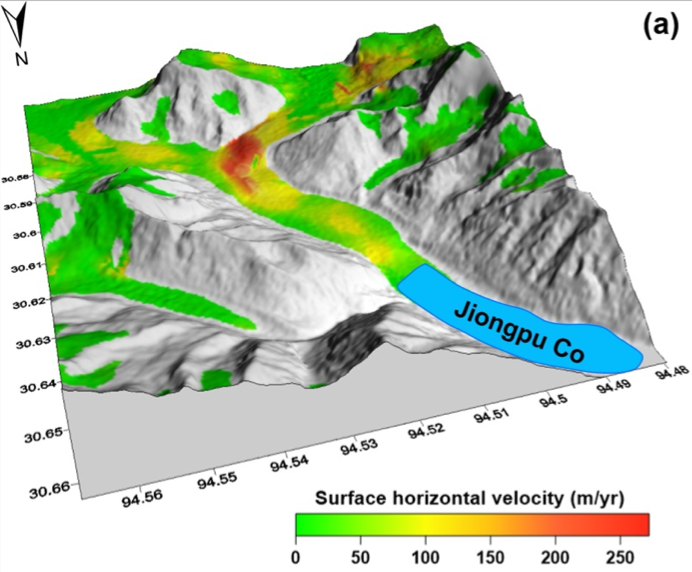
43. Studying mass movement sources and potential glacial lake outburst flood at Jiongpu Co, southeastern Tibet, using multiple remote sensing methods and HEC-RAS model
|
|
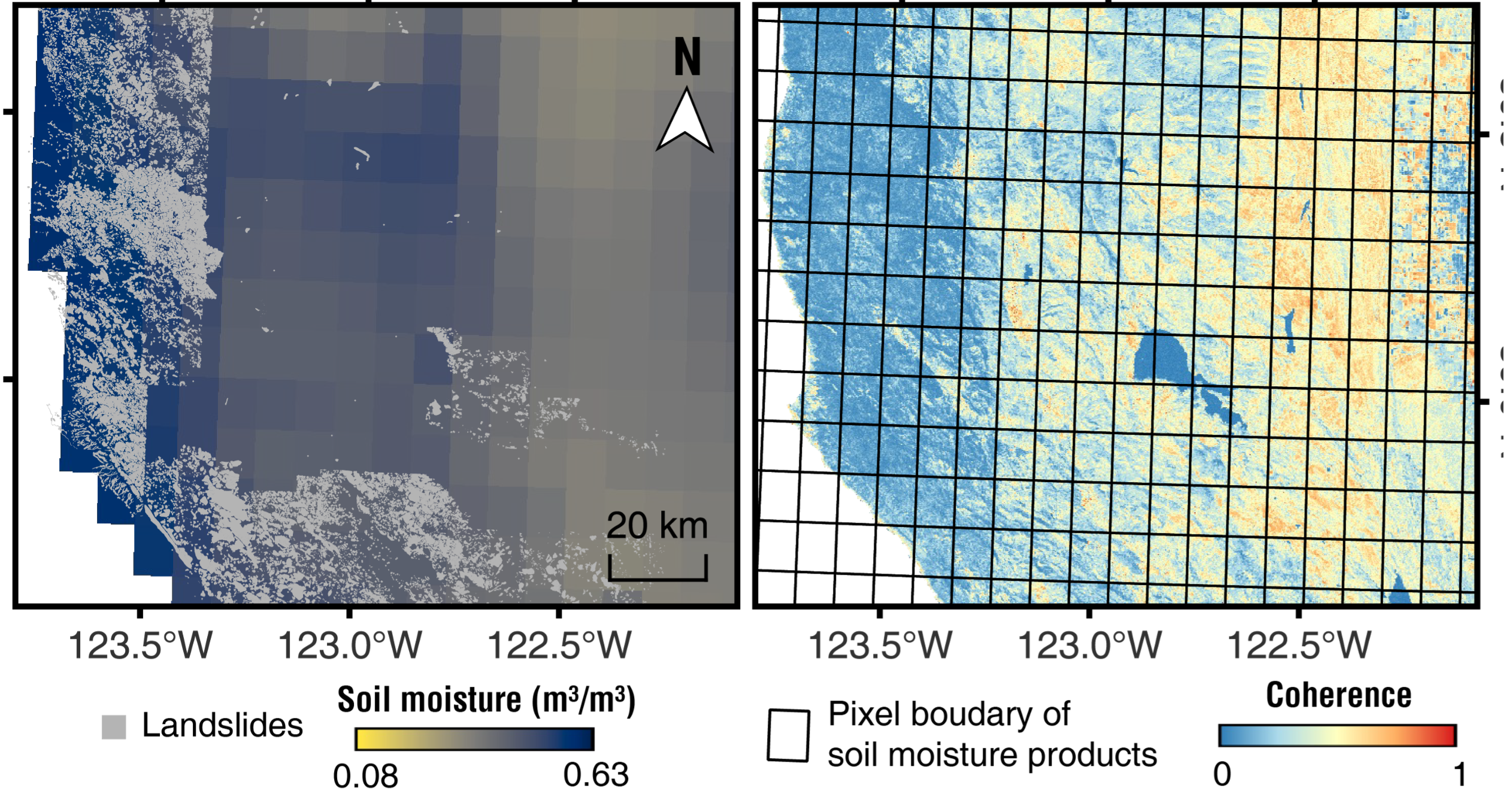
42. Hydrological proxy derived from InSAR coherence in landslide characterization
|
|
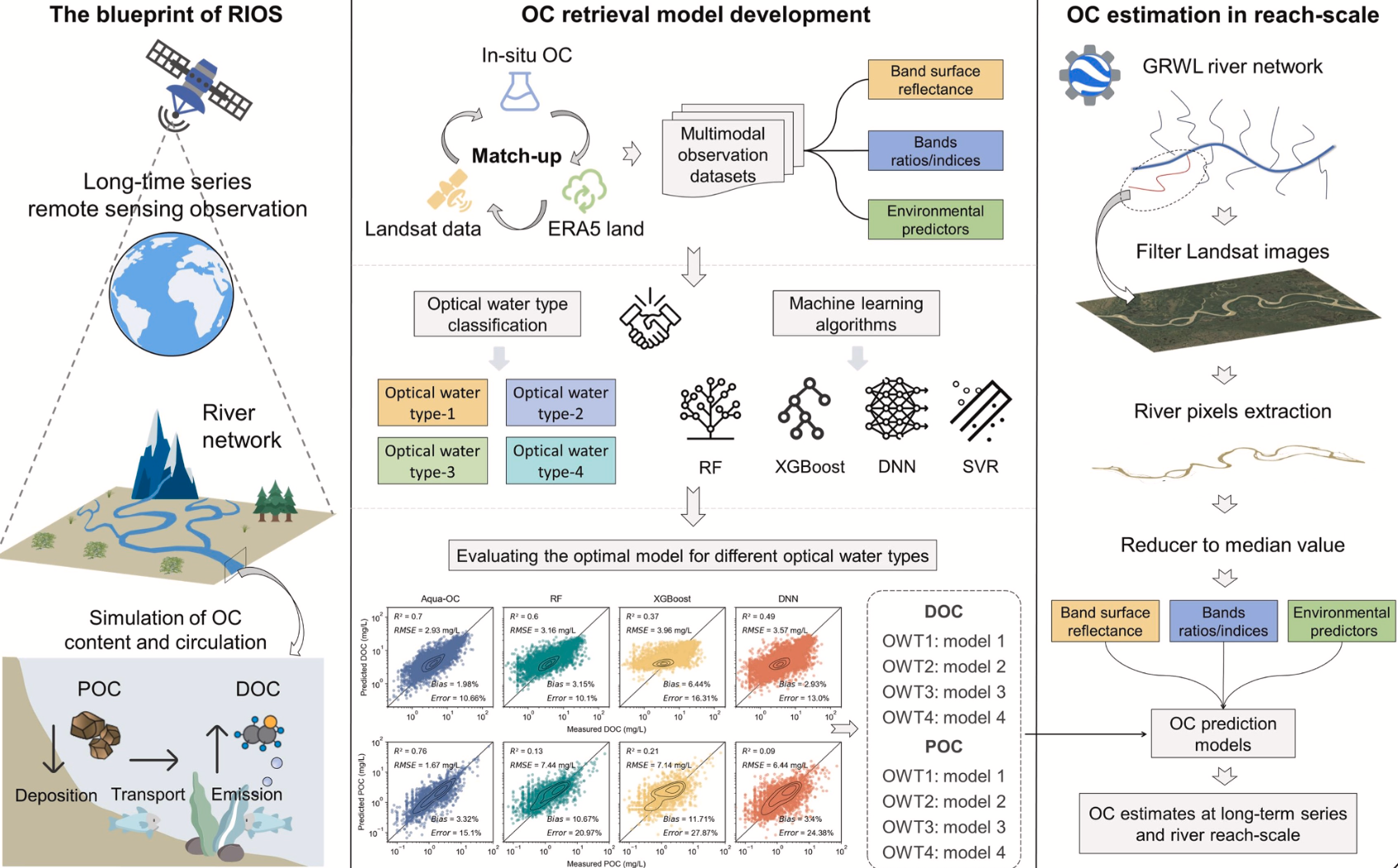
41. A novel framework for river organic carbon retrieval through satellite data and machine learning
|
|
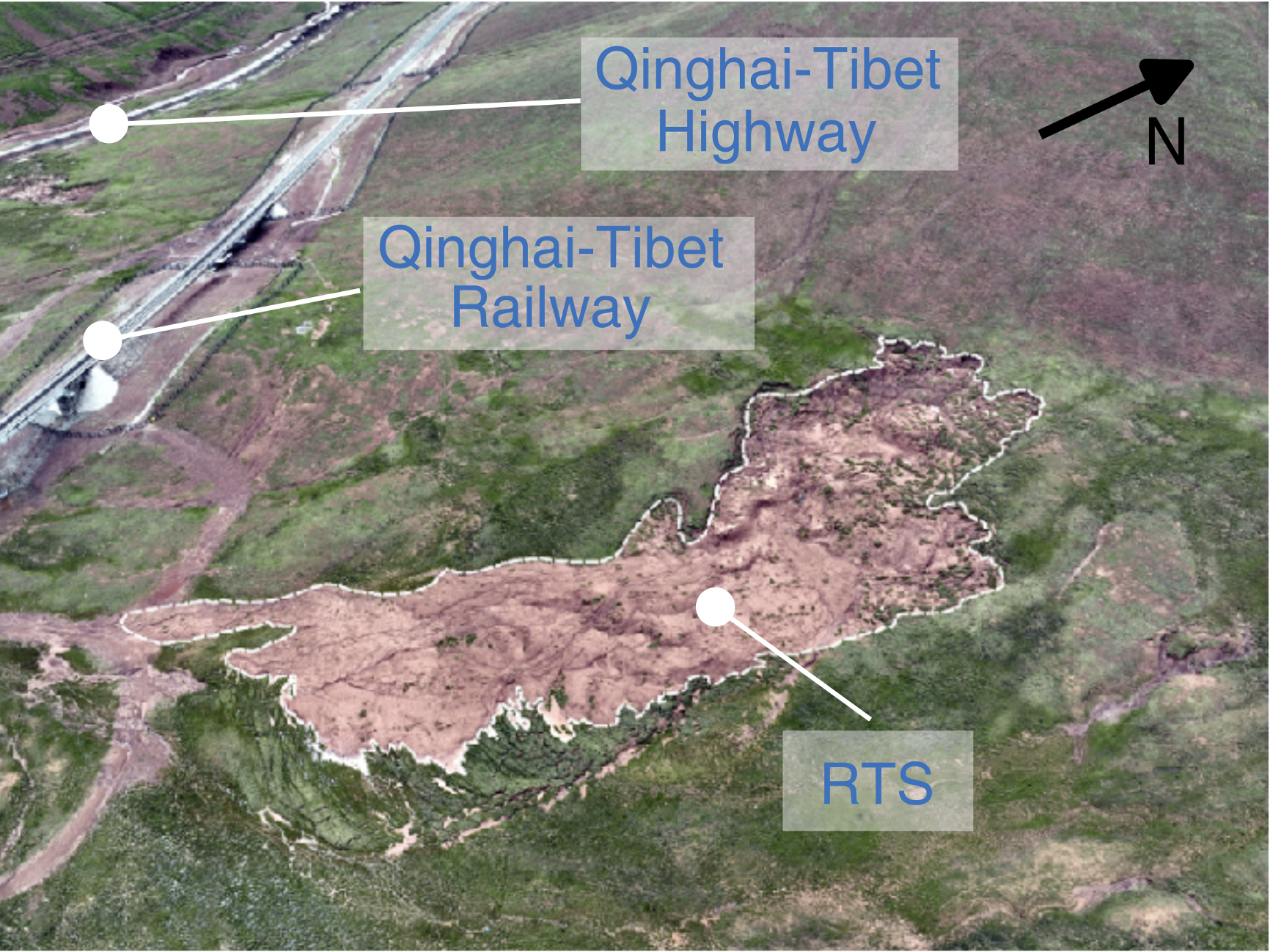
40. Multi‐annual inventorying of retrogressive thaw slumps using domain adaptation
|
|
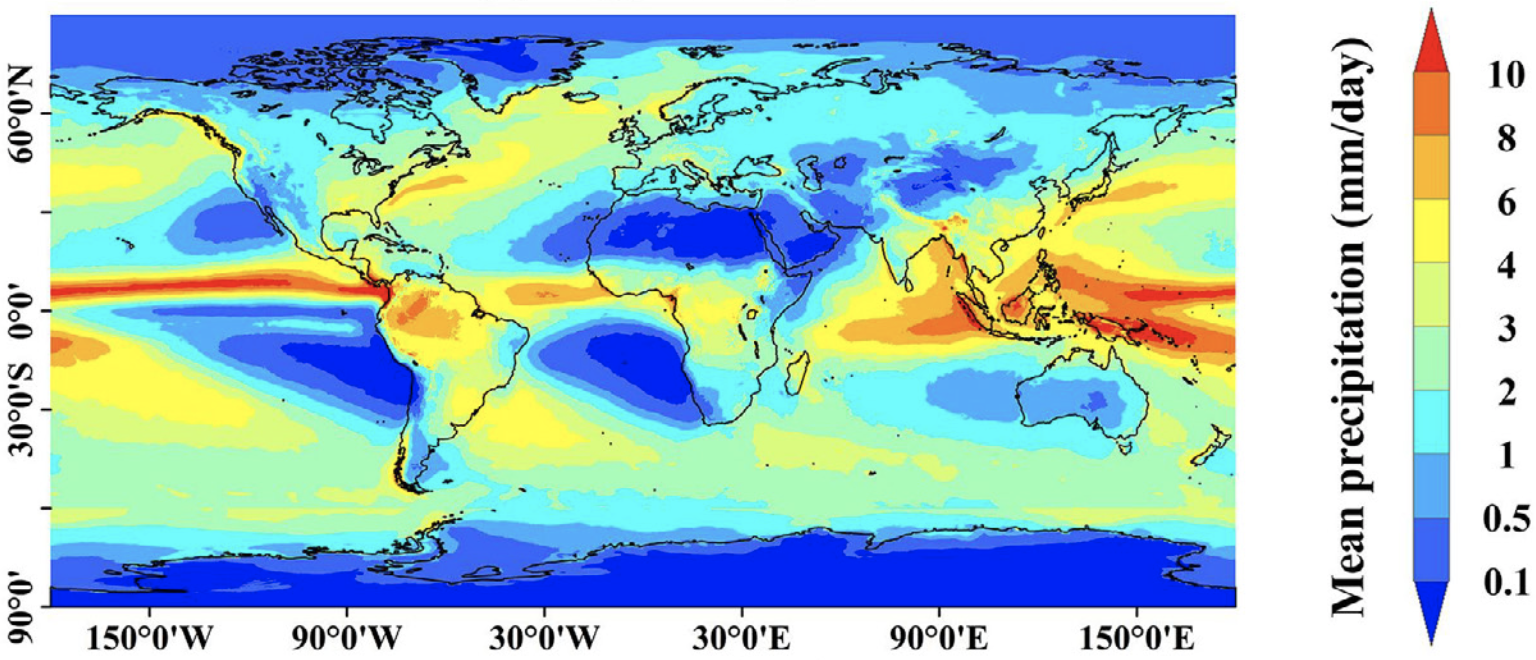
39. GMCP: A fully Global multi-source Merging-and-Calibration Precipitation dataset (1-hourly, 0.1°, global, 2000–Present)
|
|
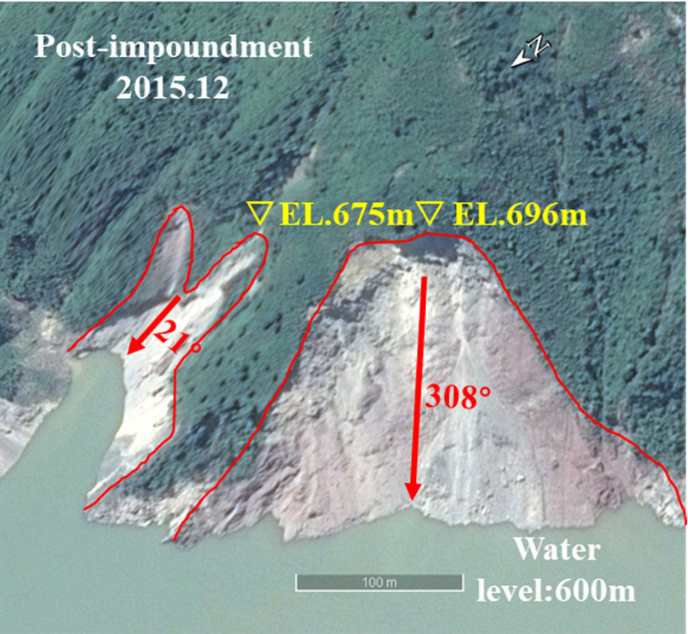
38. The influence of reservoirs on landslide erosion
|
2024
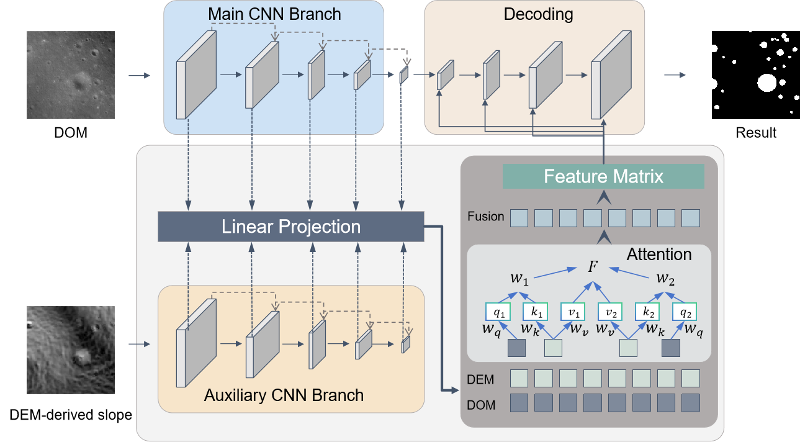
|
37. Dual-branch multi-modal convergence for crater detection using Chang’e image
|
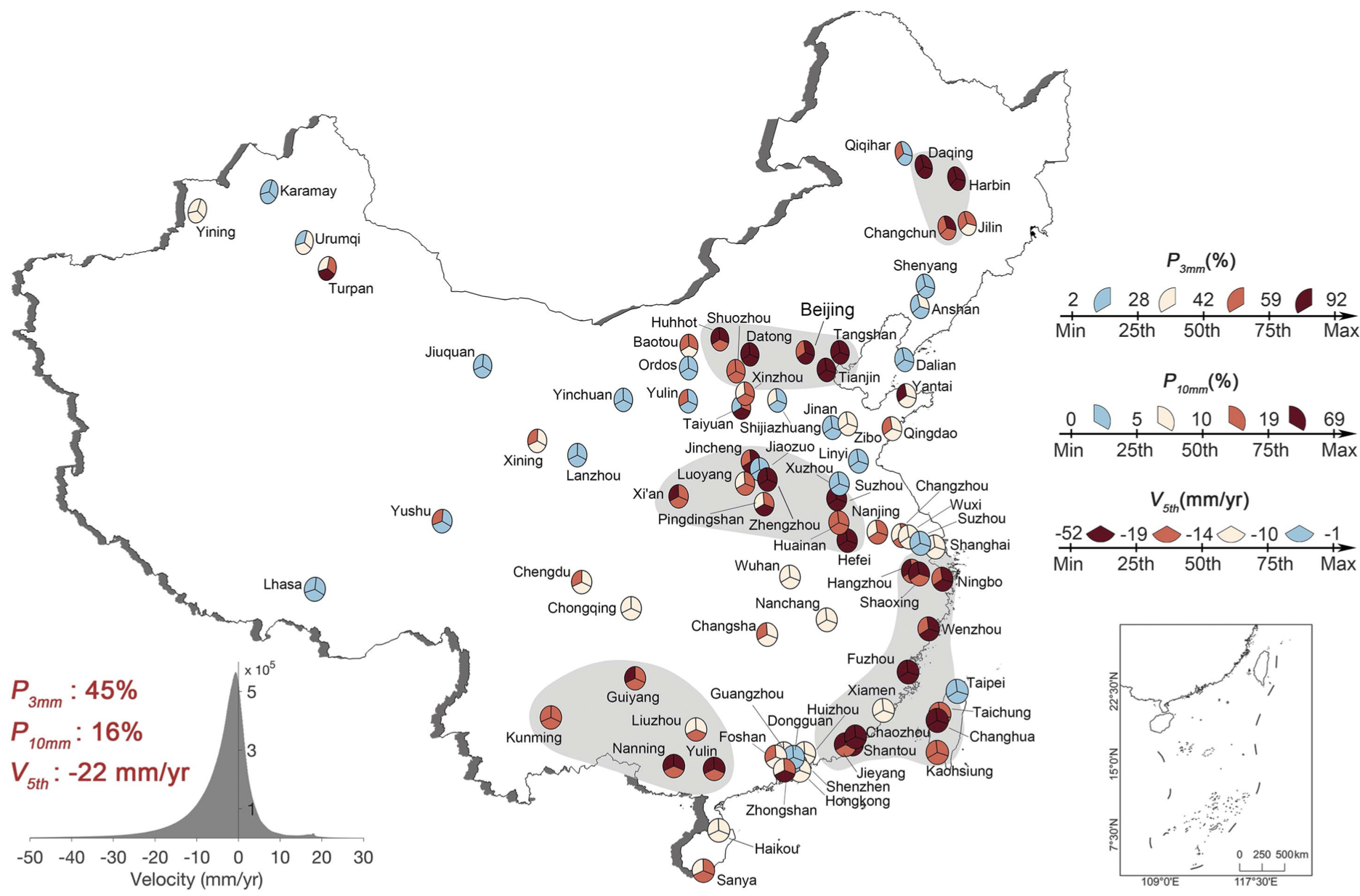
|
36. A national-scale assessment of land subsidence in China’s major cities
|
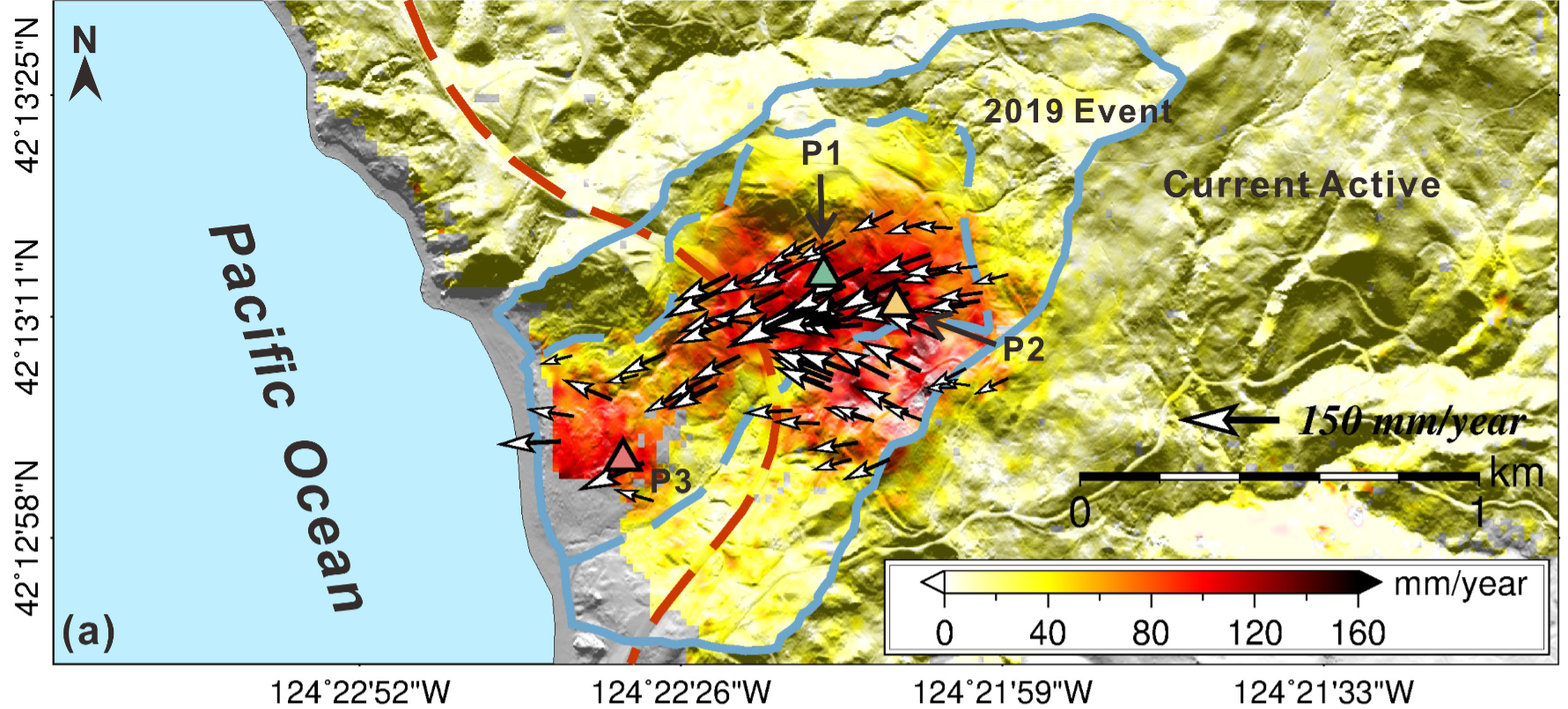
|
35. Enhancing 4-D landslide monitoring and block interaction analysis with a novel Kalman-Filter-Based InSAR approach
|
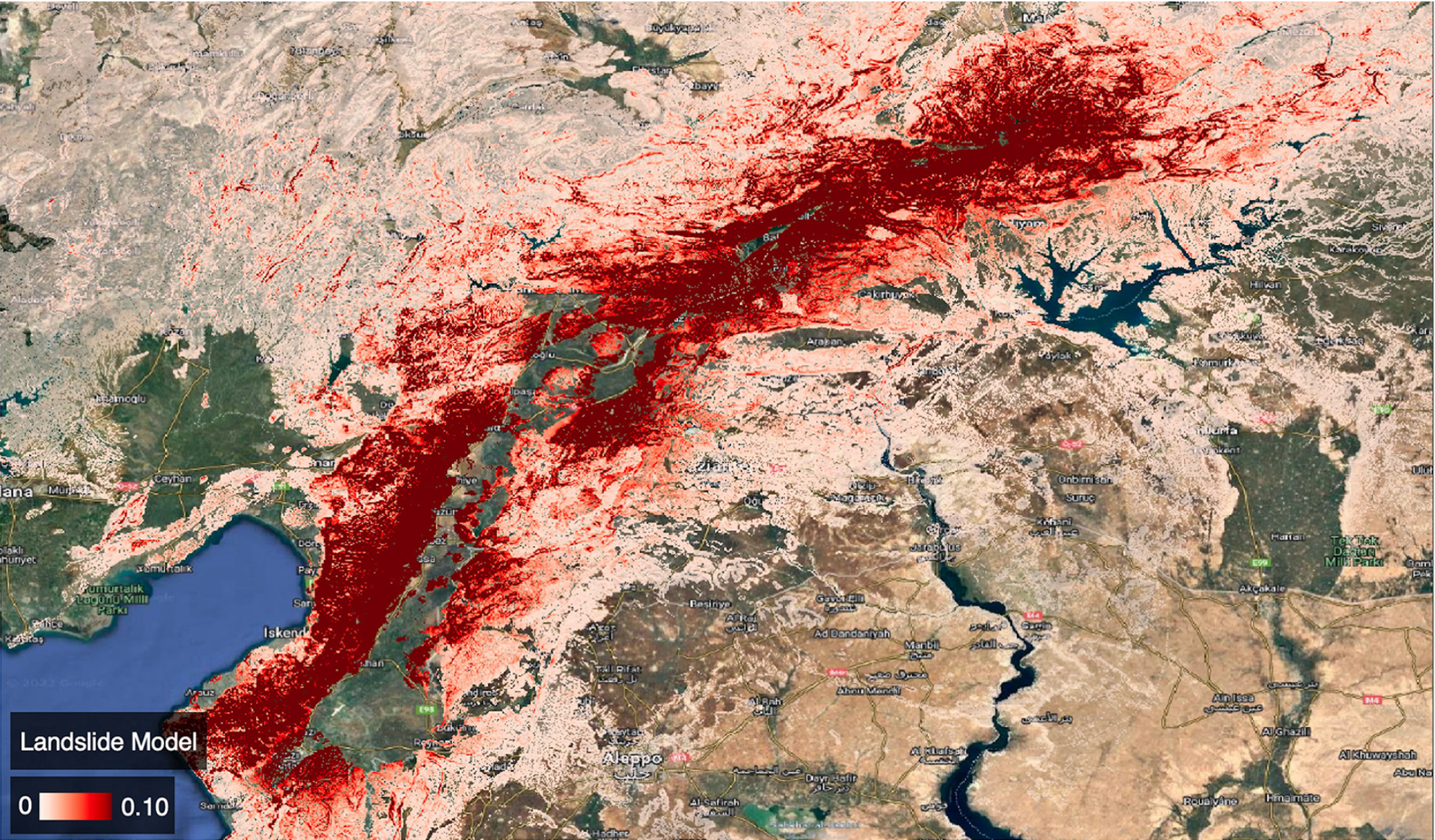
|
34. Rapid building damage estimates from the M7.8 Turkey Earthquake sequence via causality-informed Bayesian inference from satellite imagery
|
|
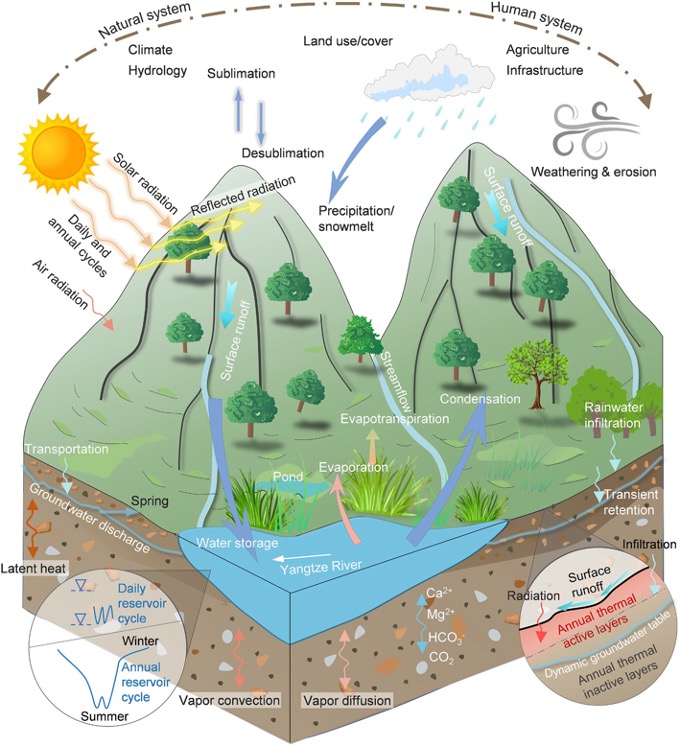
33. Near-surface soil hydrothermal response feedbacks landslide activity and mechanism
|
|
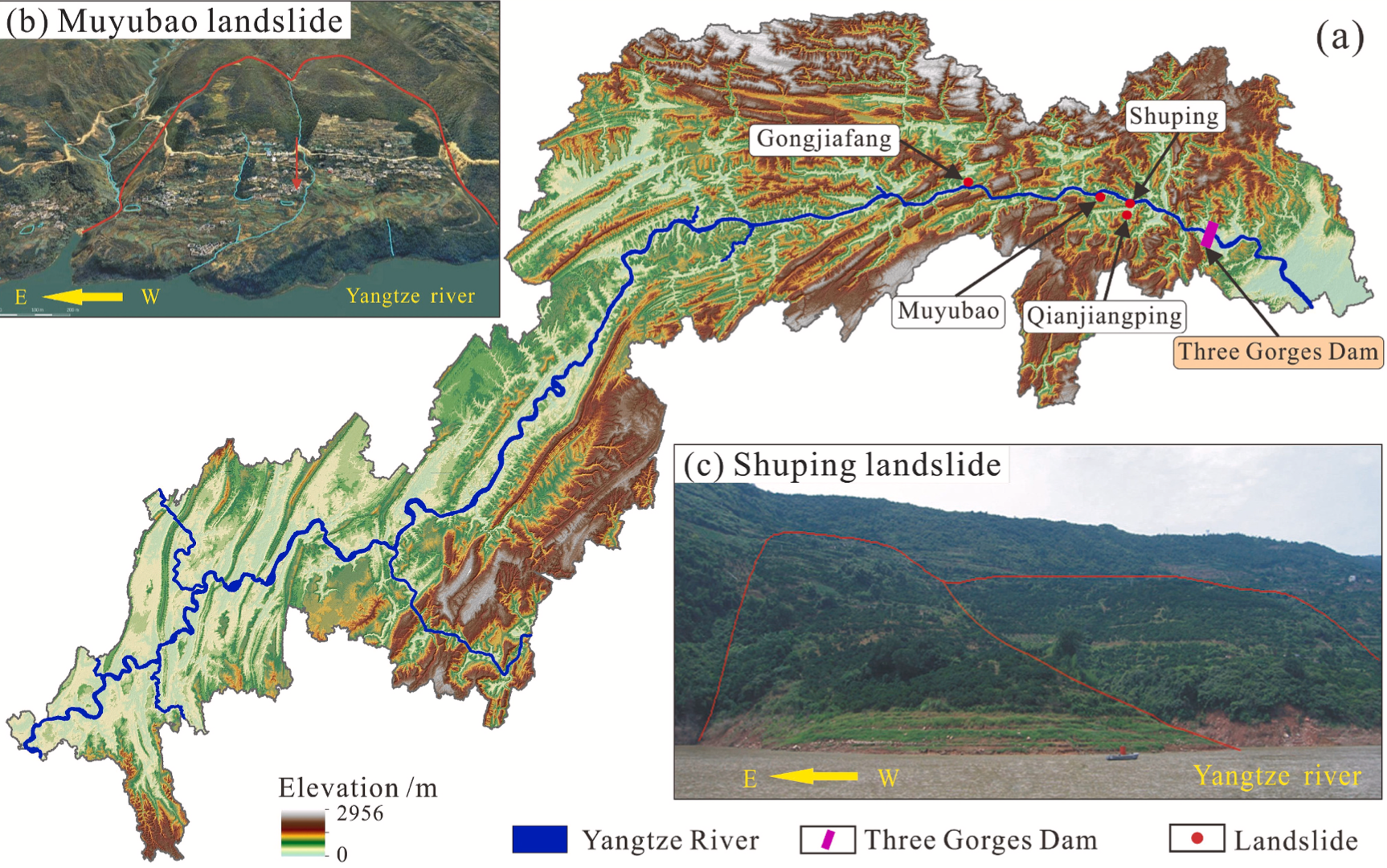
32. A novel framework for landslide displacement prediction using MT-InSAR and machine learning techniques
|
|
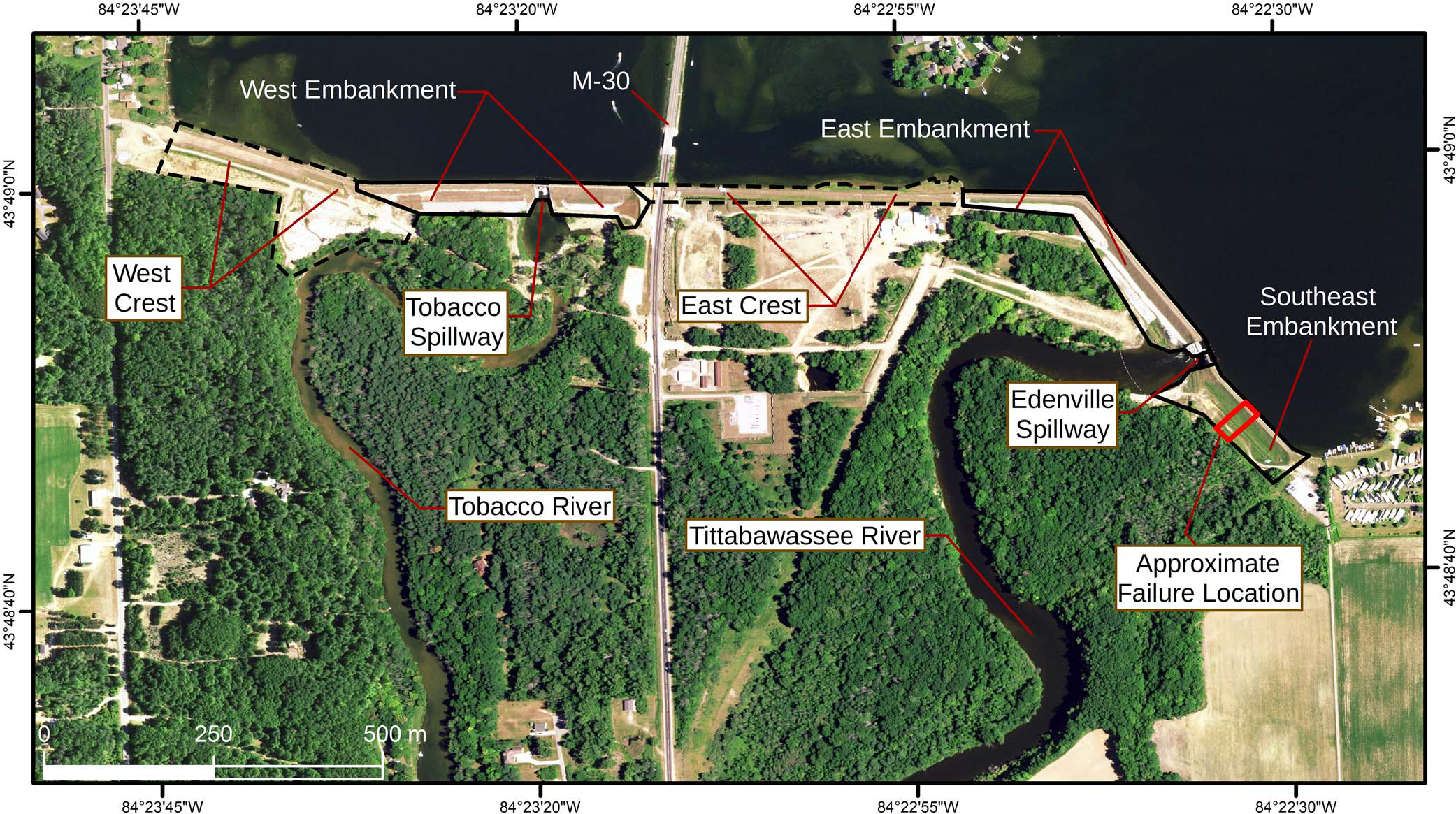
31. Need for a multi-sensor monitoring approach for embankment failures: lessons learned from the Edenville Dam failure
|
|
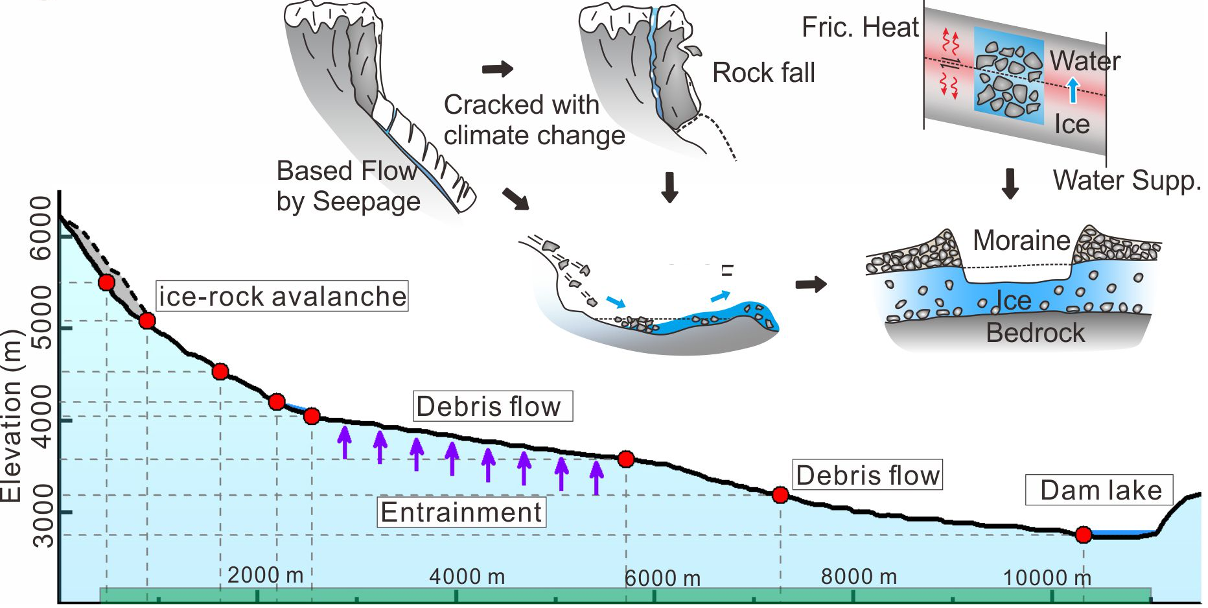
30. Glacier retreat in Eastern Himalaya drives catastrophic glacier hazard chain
|
|
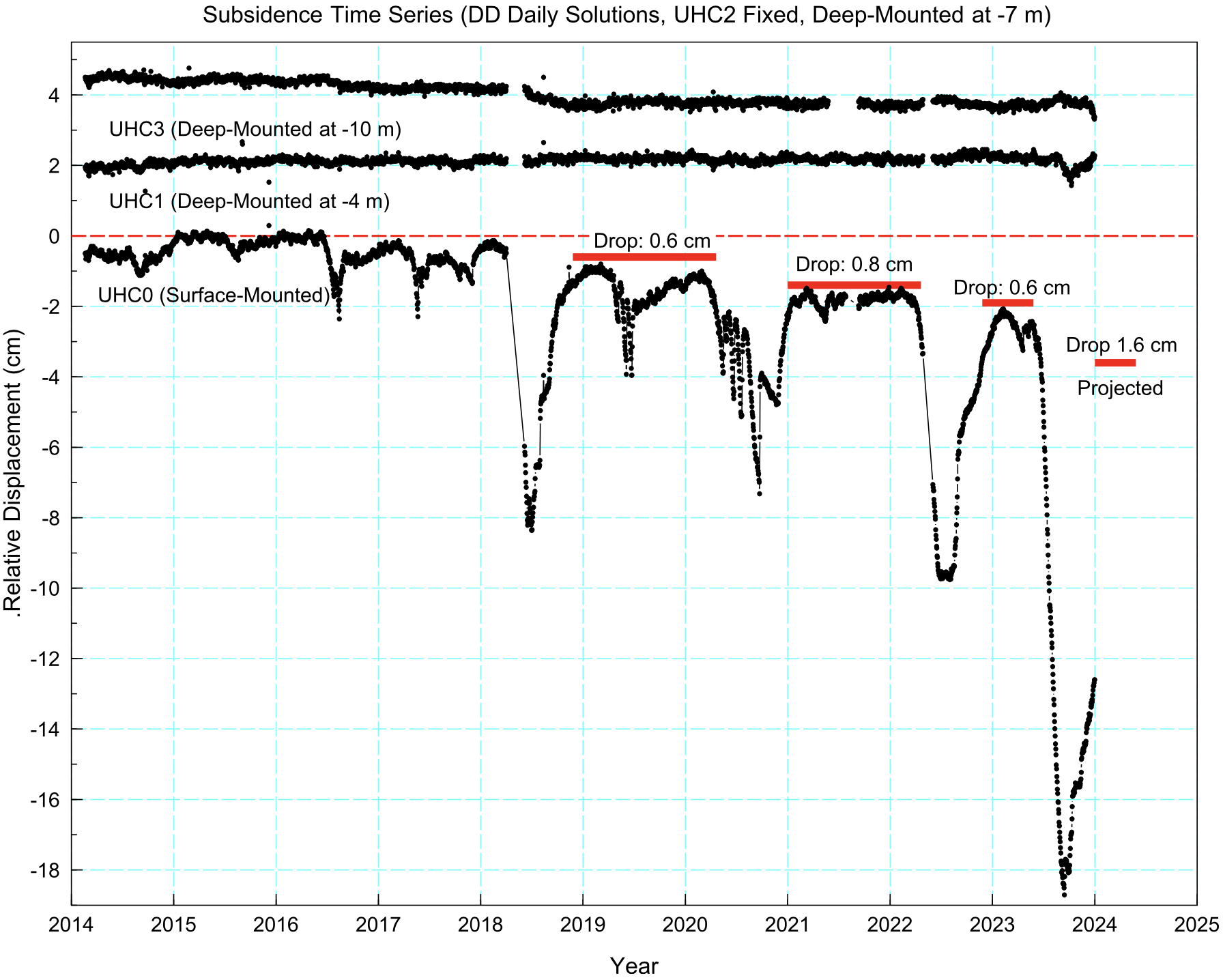
29. Unveiling the hidden threat: drought-induced inelastic subsidence in expansive soils
|
|
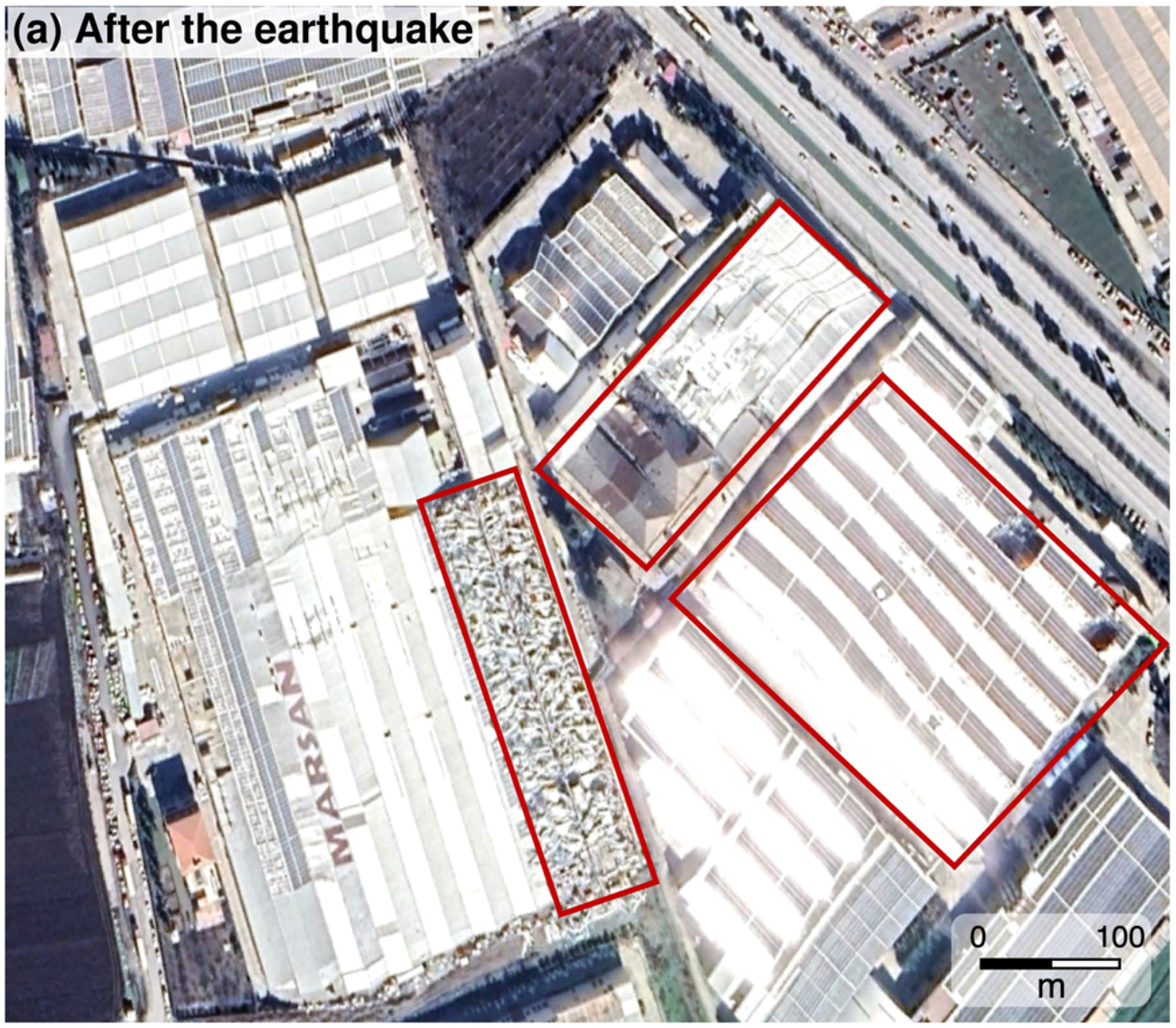
28. Intelligent assessment of land surface damage in 2023 Turkey-Syria Earthquake by multiple remote sensing observations
|
|
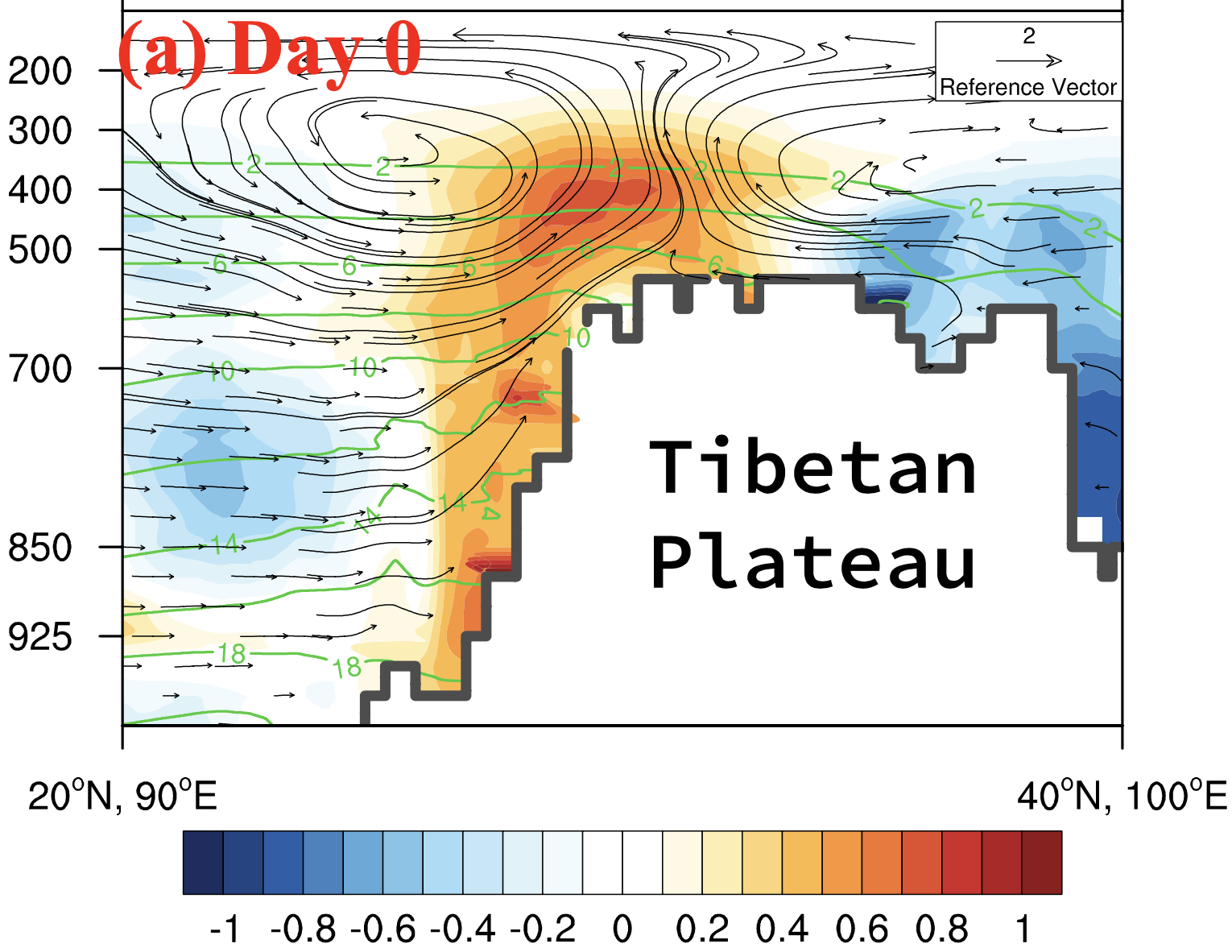
27. Investigation of precipitation process in the water vapor channel of the Yarlung Zsangbo Grand Canyon
|

|
26. The locality-adaptation theory of traditional villages
|
2023
|
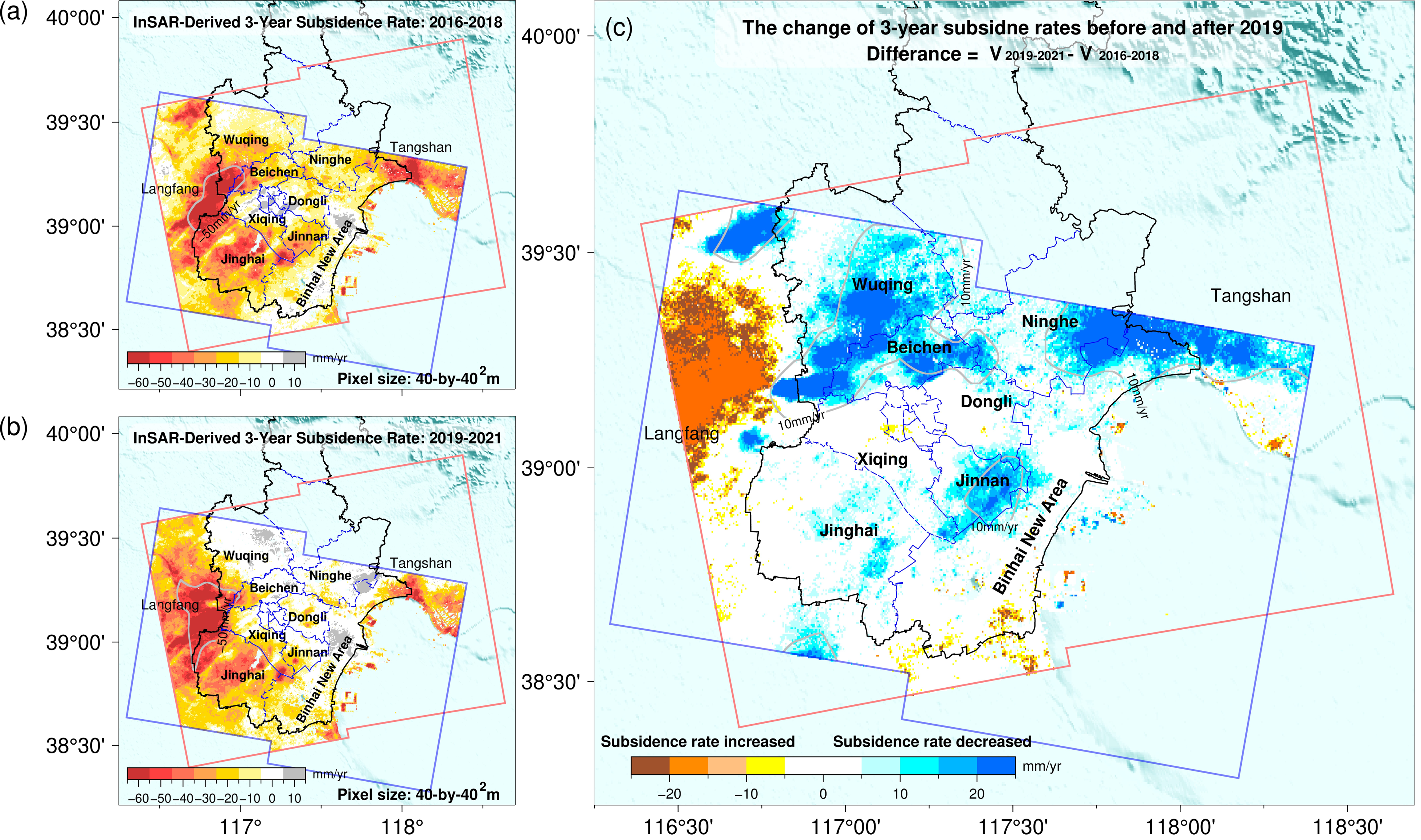
25. Land Subsidence in Tianjin, China: Before and after the South-to-North Water Diversion
|
|
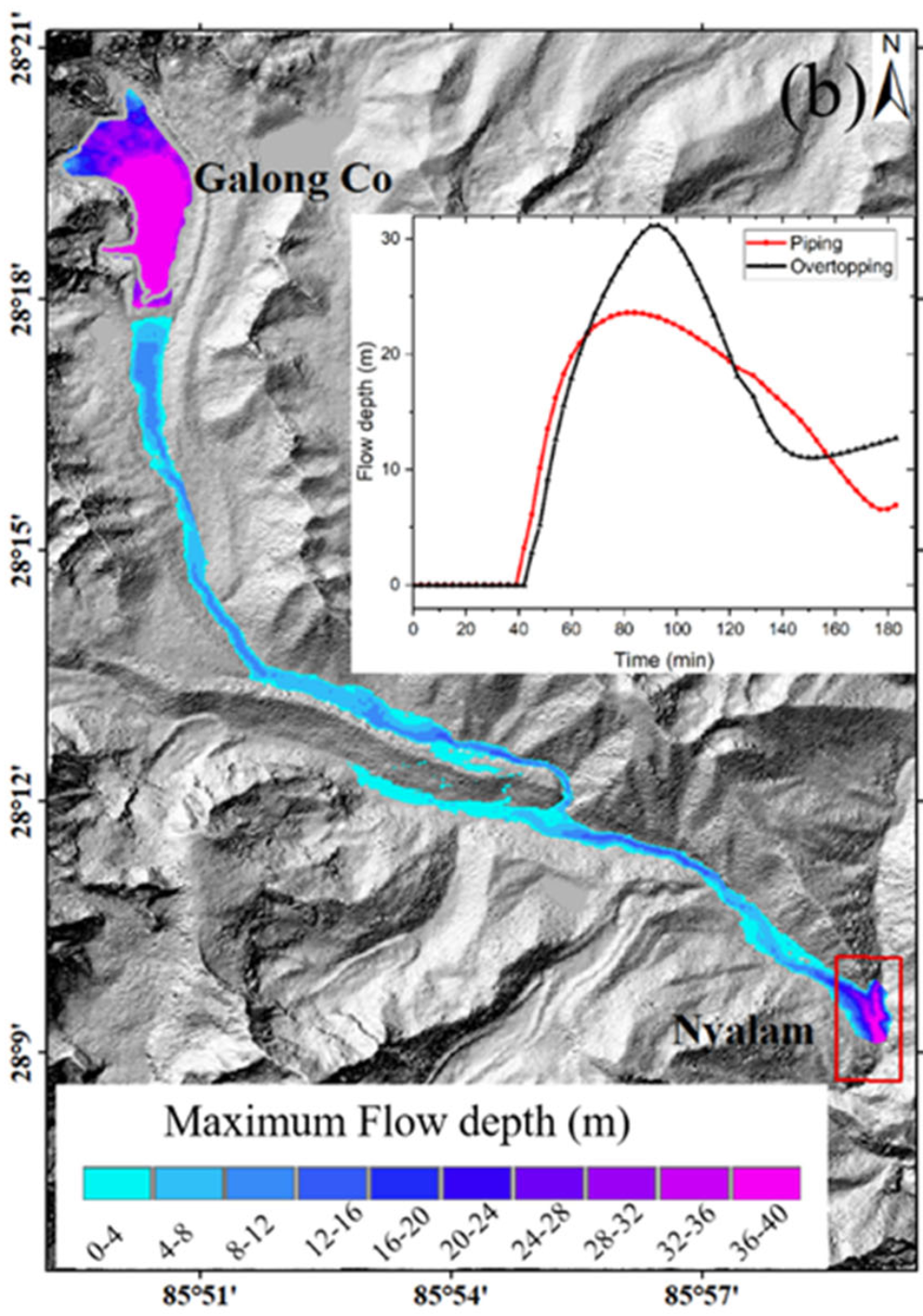
24. Glacial lake outburst hazard monitoring and flooding modeling by integrating multiple remote sensing methods and HEC-RAS
|
|
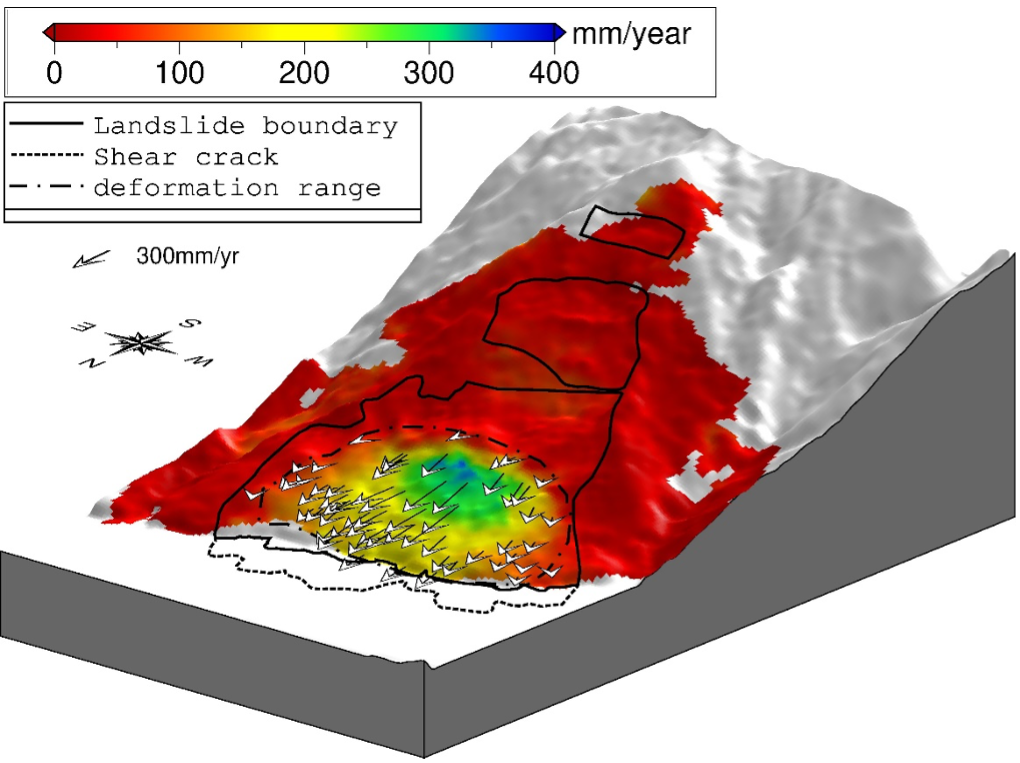
23. Enhanced Kinematic Inversion of 3-D Displacements, Geometry, and Hydraulic Properties of a North-South Slow-Moving Landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir
|
|
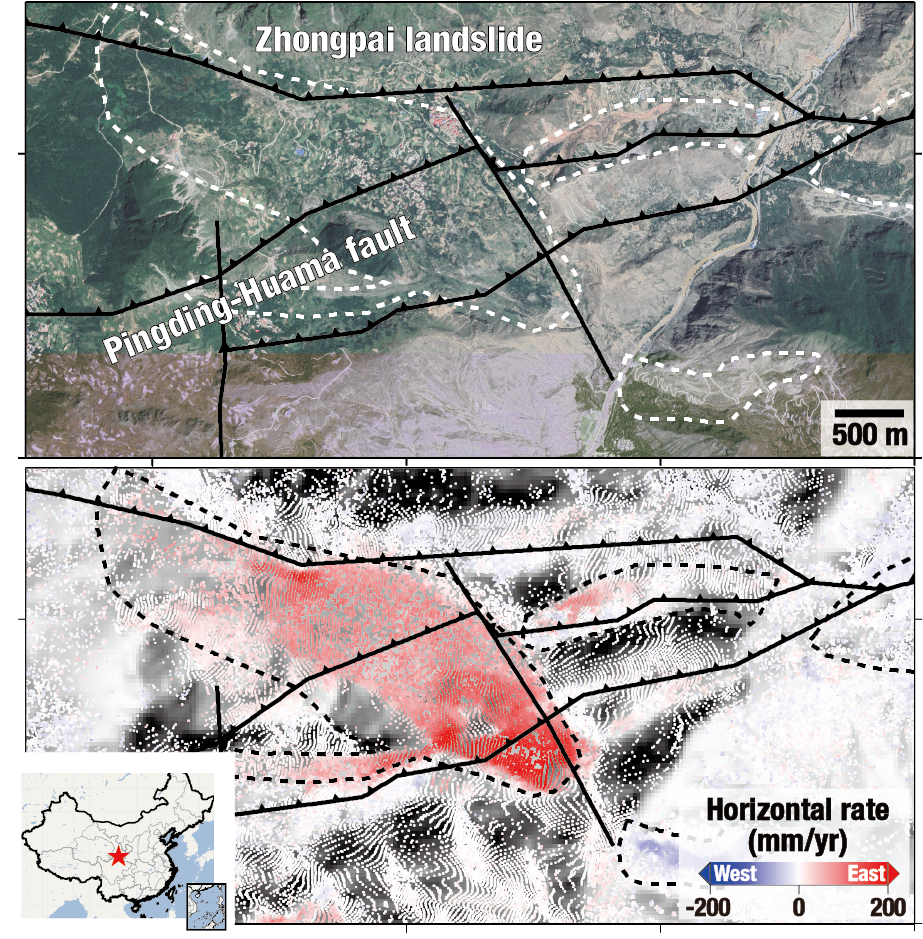
22. Characterization of landslide displacements in an active fault zone in Northwest China
|
2022
|
21. Collapse and subsidence mechanism of compacted loess and suitability of mountain bulldozing and city creation projects in the Loess Plateau of China
|
|
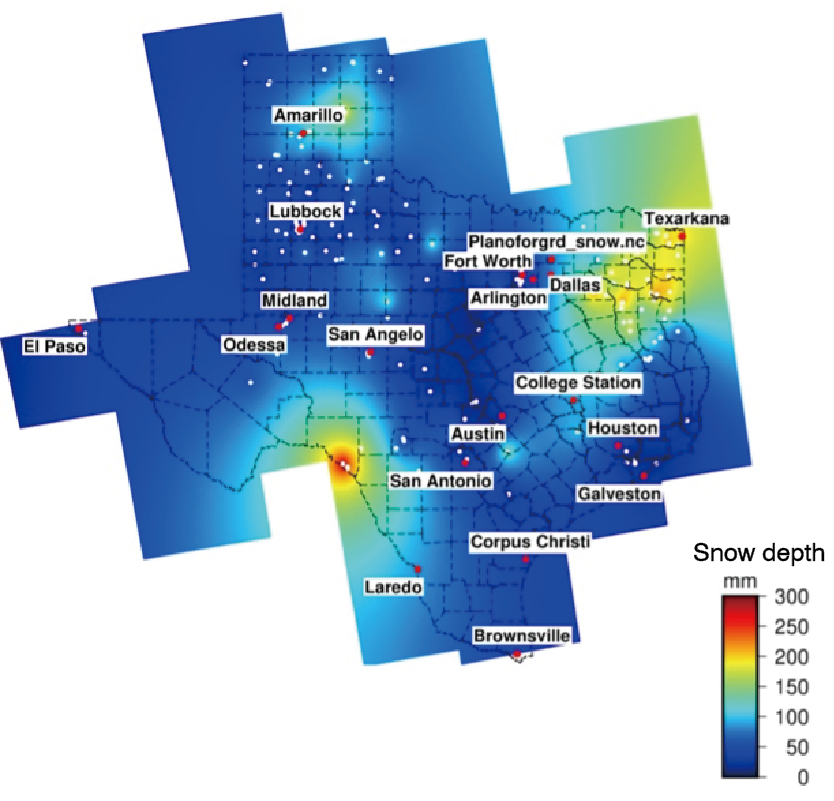
20. Machine-learning estimation of snow depth in 2021 Texas statewide winter storm using SAR imagery
|
|
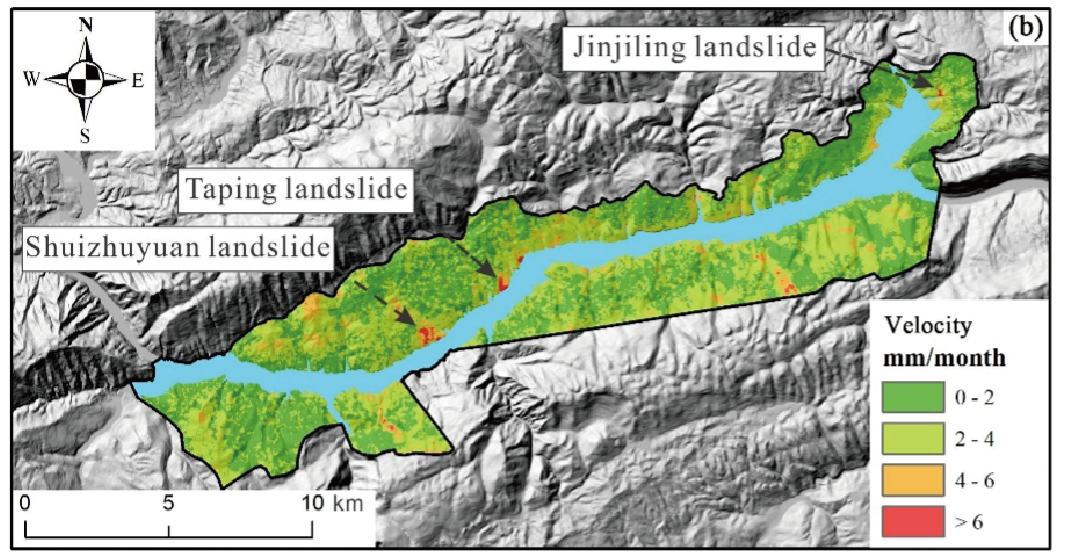
19. Enhanced dynamic landslide hazard assessment using MT-InSAR method in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area
|
2021
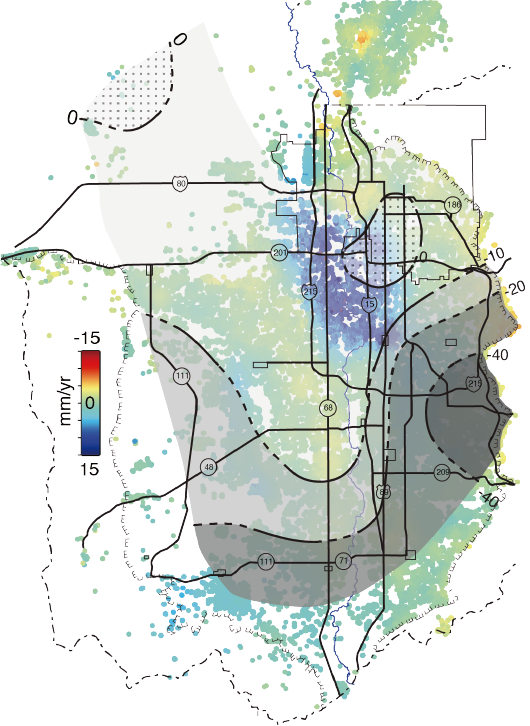
|
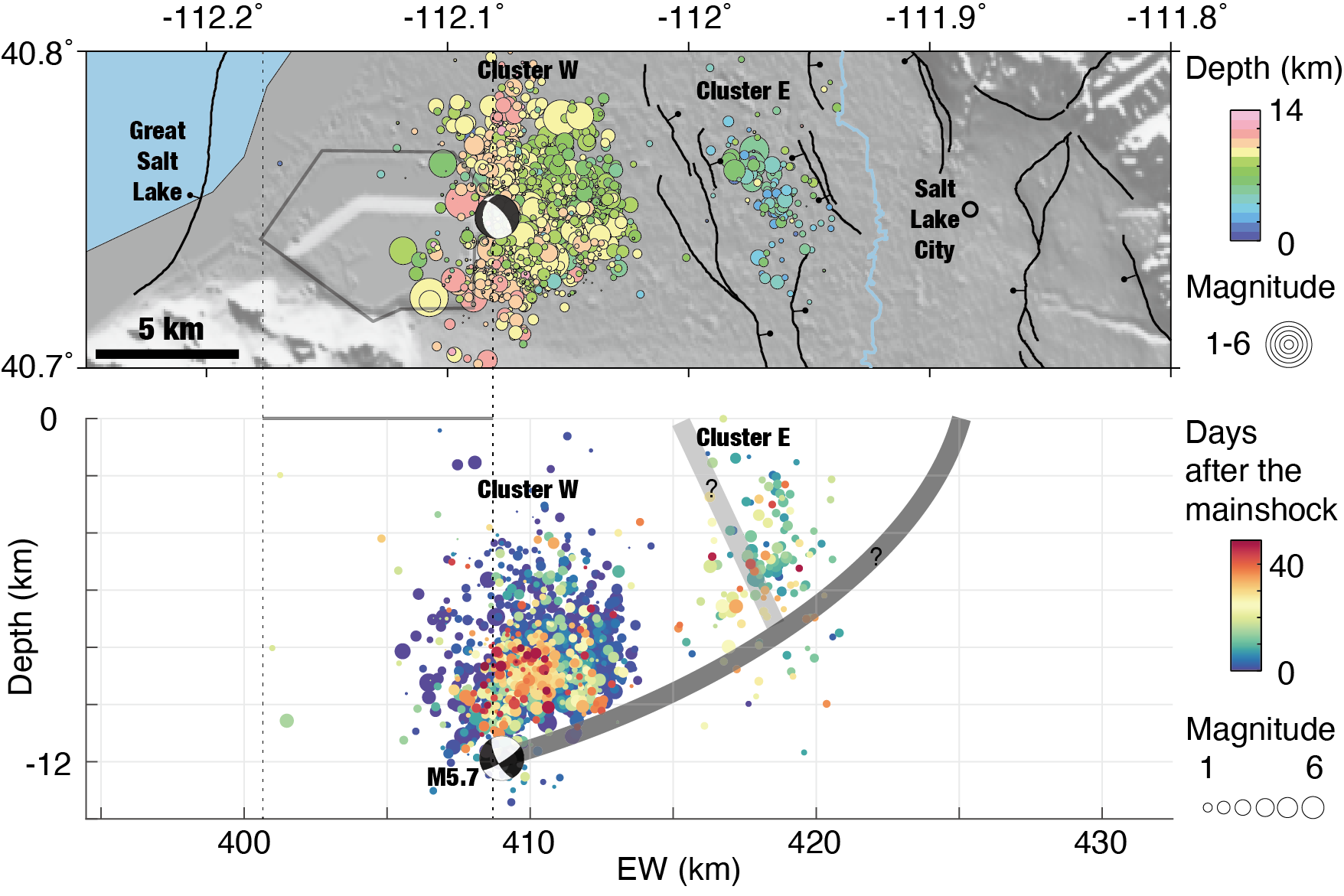
18. Stress perturbations from hydrological and industrial loads and seismicity in the Salt Lake City region
|
|
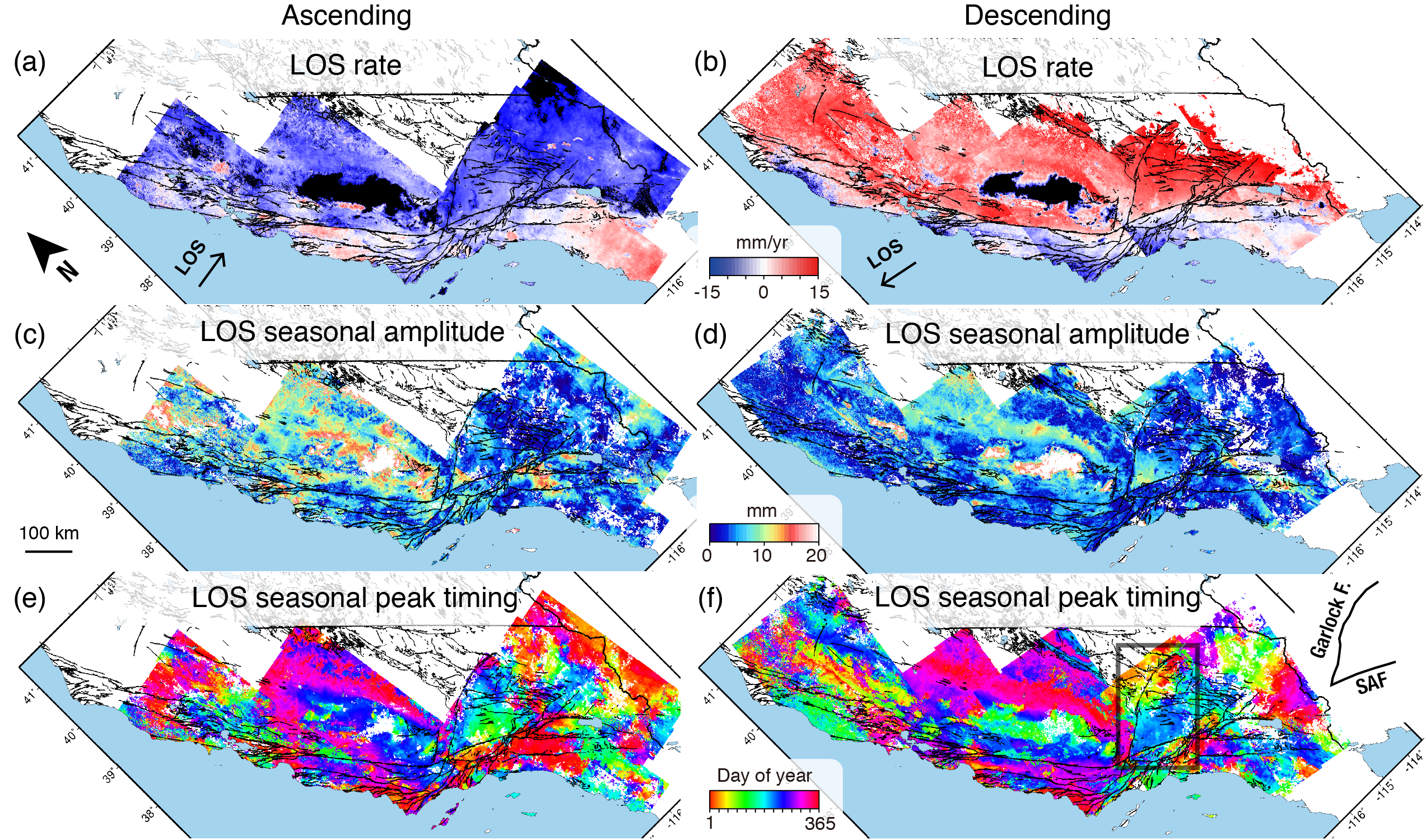
17. Machine-learning characterization of tectonic, hydrological and anthropogenic sources of ground deformation in California
|
|
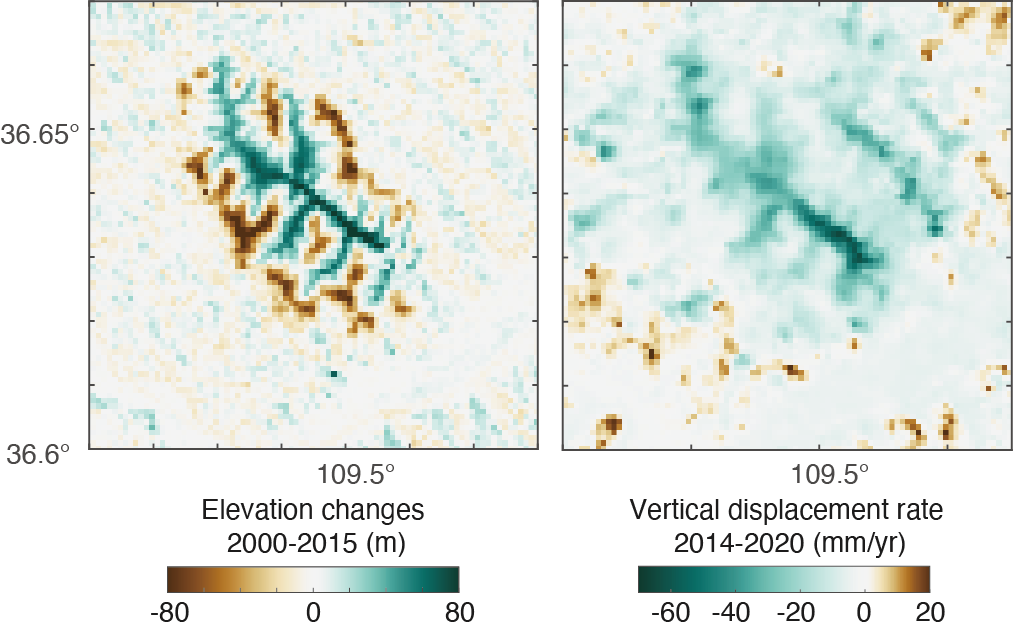
16. Remote sensing characterization of mountain excavation and city construction in loess plateau
|
|
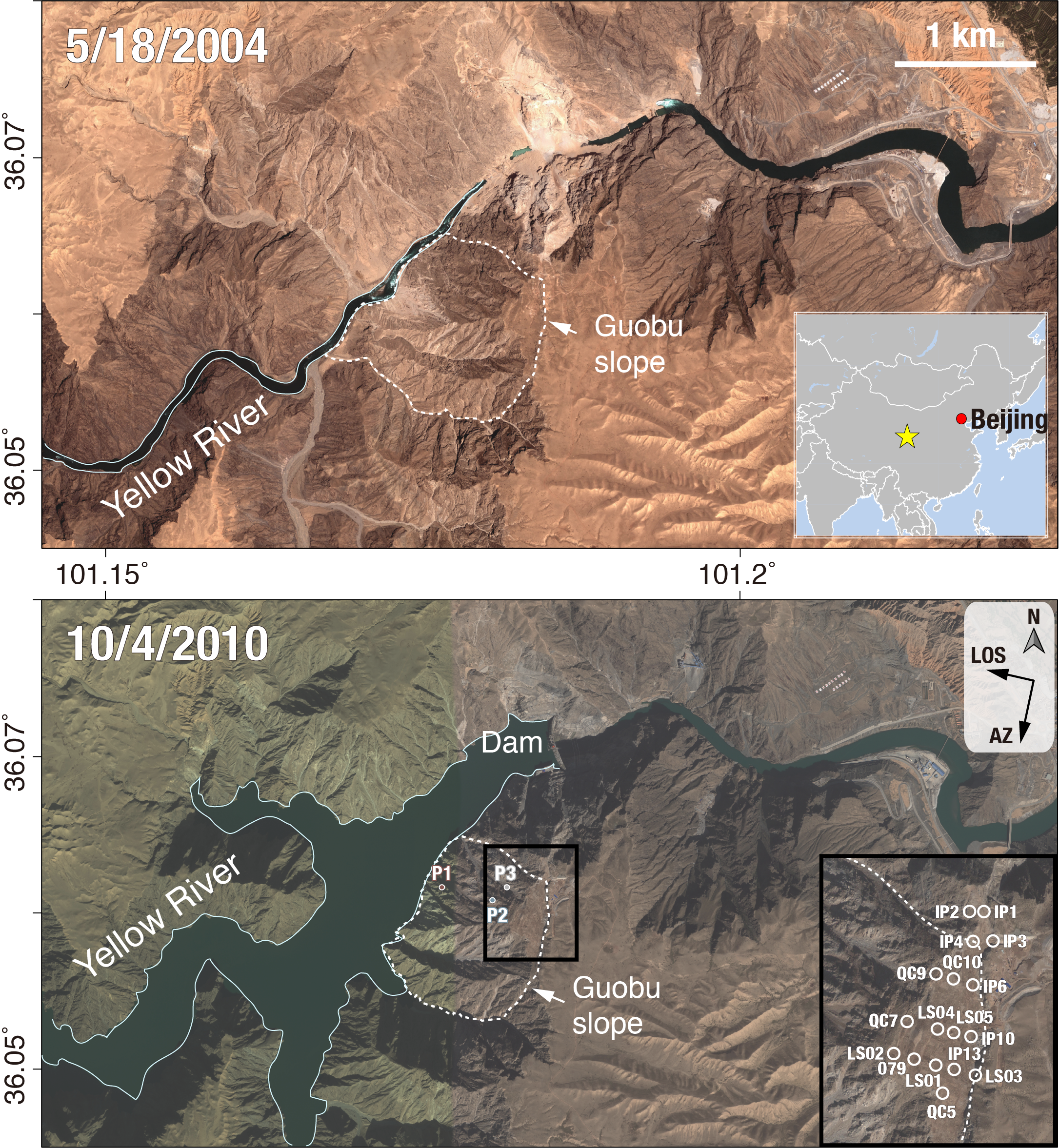
15. Hydrological control shift from river level to rainfall in the reactivated Guobu Slope besides the Laxiwa hydropower station (China)
|
|
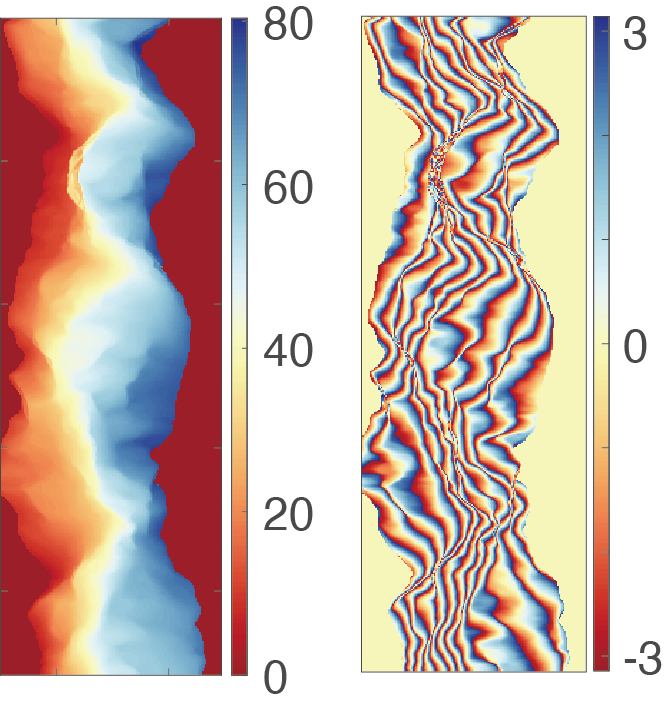
14. Knowledge-aided InSAR phase unwrapping approach
|
|
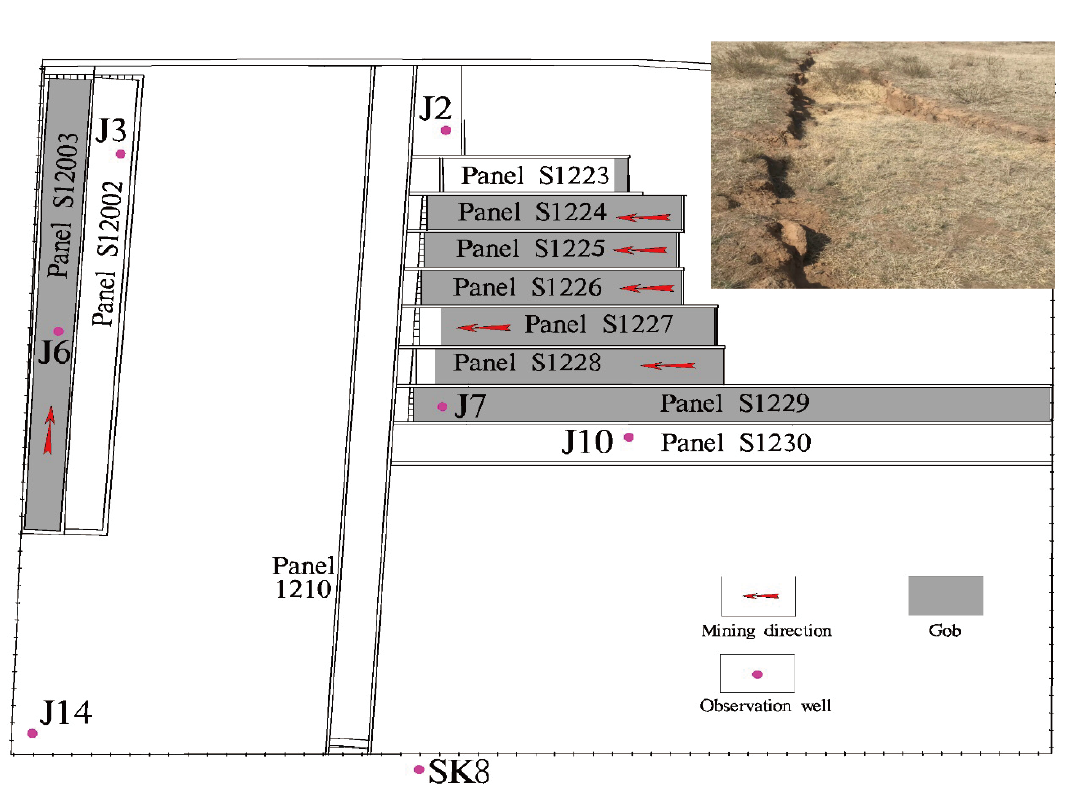
13. Hydro-mechanical coupling in the shallow crust – insight from groundwater level and satellite radar imagery in a mining area
|
2020
|
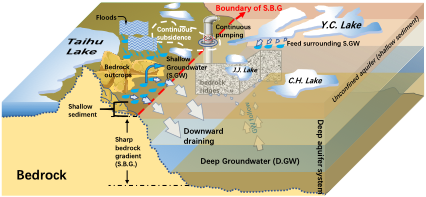
12. Surface response and subsurface features during the restriction of groundwater exploitation in Suzhou (China) inferred from decadal SAR interferometry
|
|
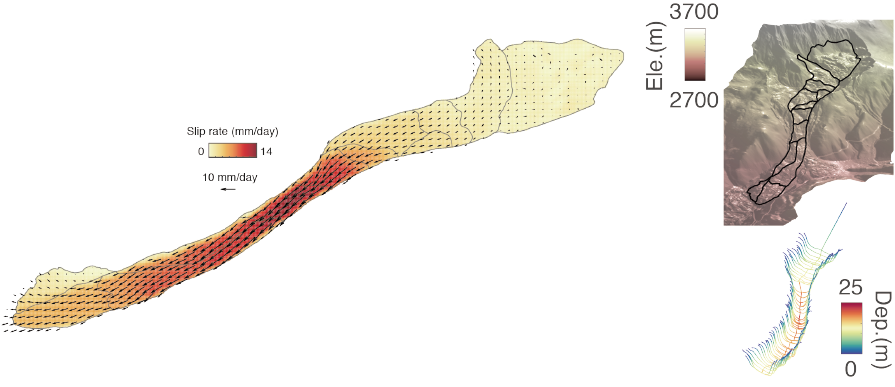
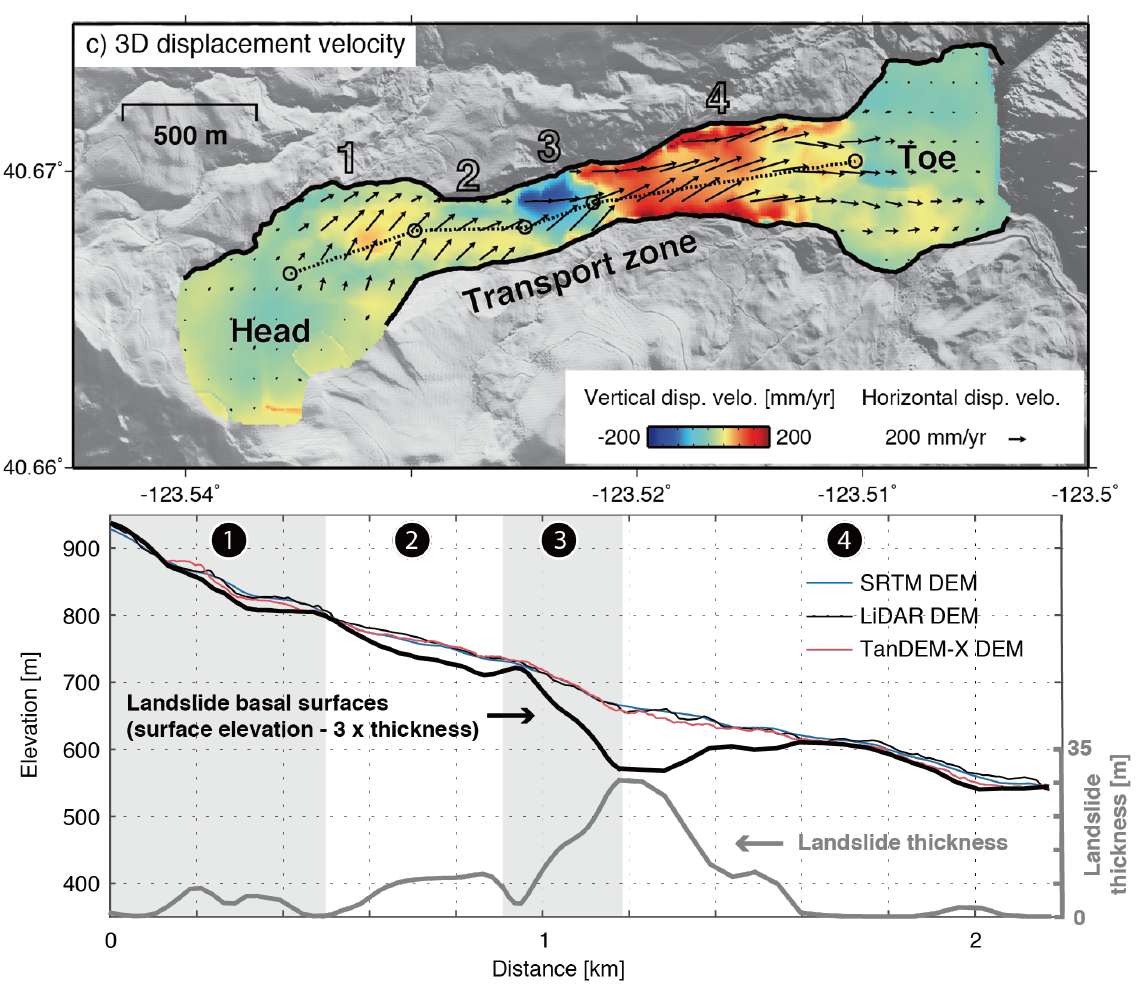
11. Four-dimensional surface motions of the Slumgullion landslide and quantification of hydrometeorological forcing
|
|
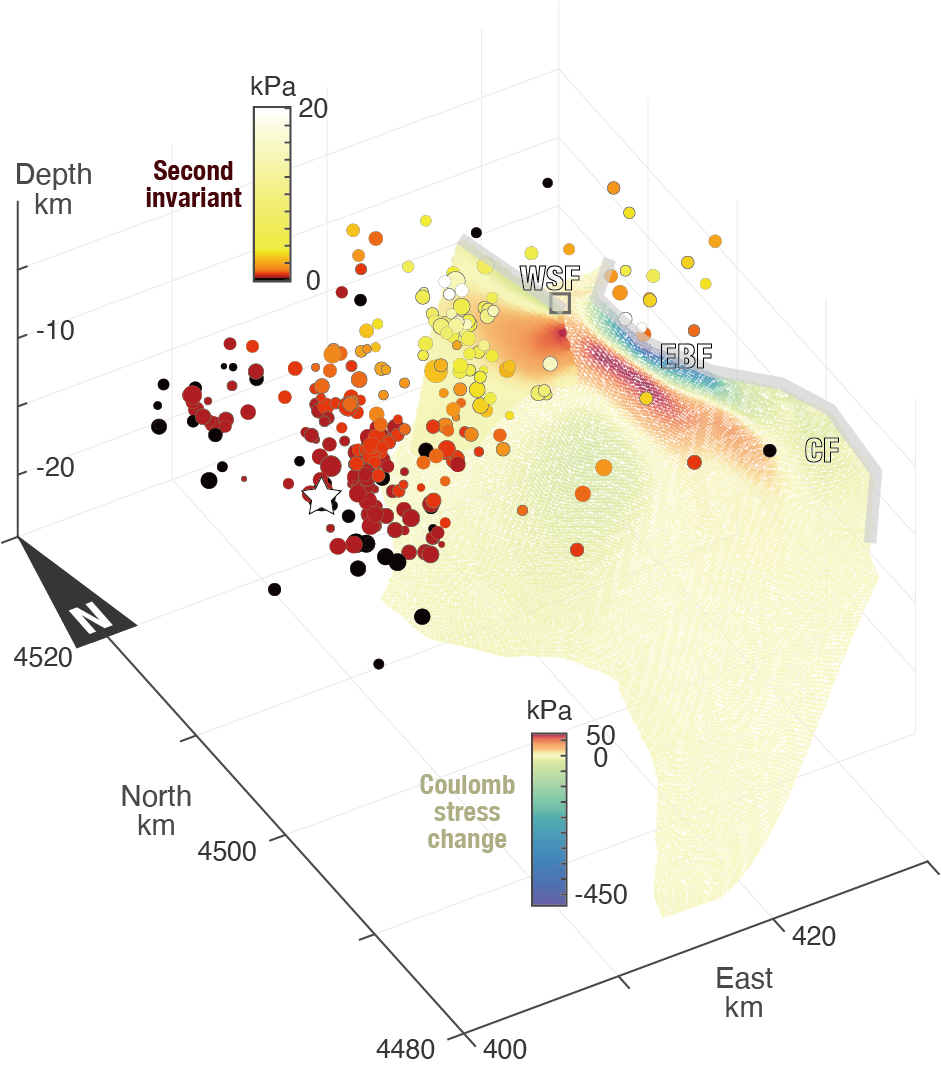
10. Aquifer dynamics in the seismically hazardous Salt Lake Valley, Utah, USA.
|
|
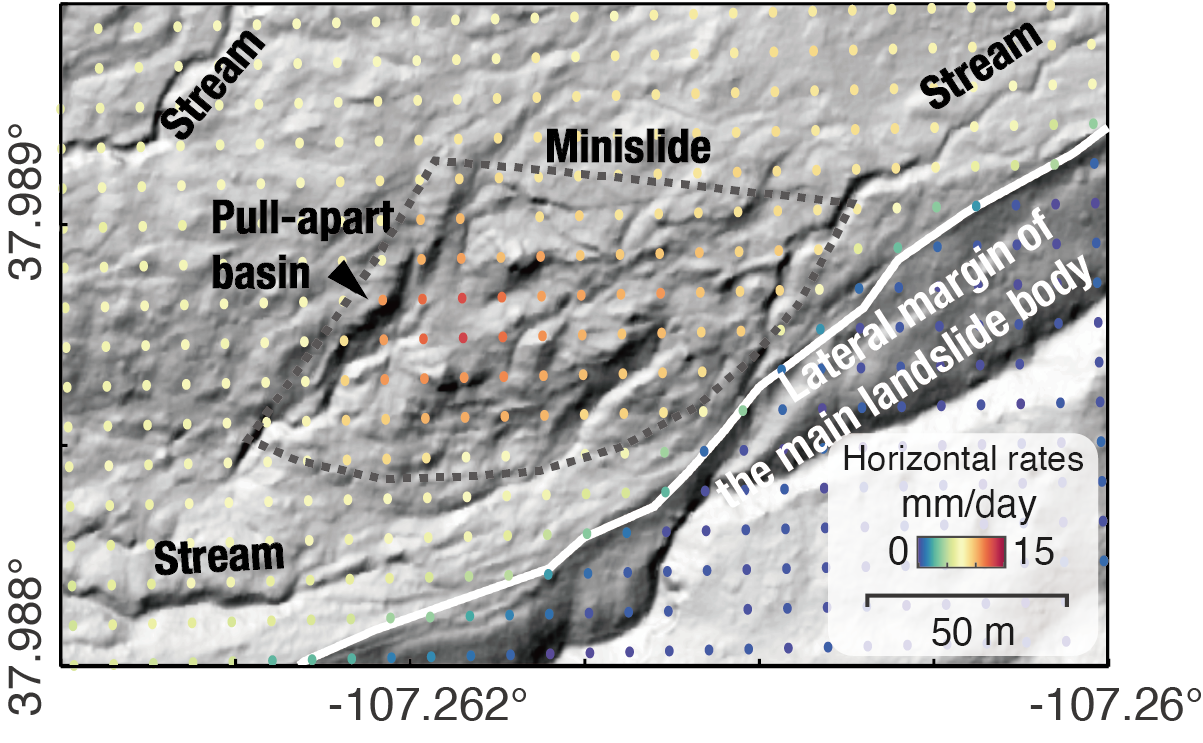
9. Internal kinematics of the Slumgullion landslide (USA) from high-resolution UAVSAR InSAR data
|
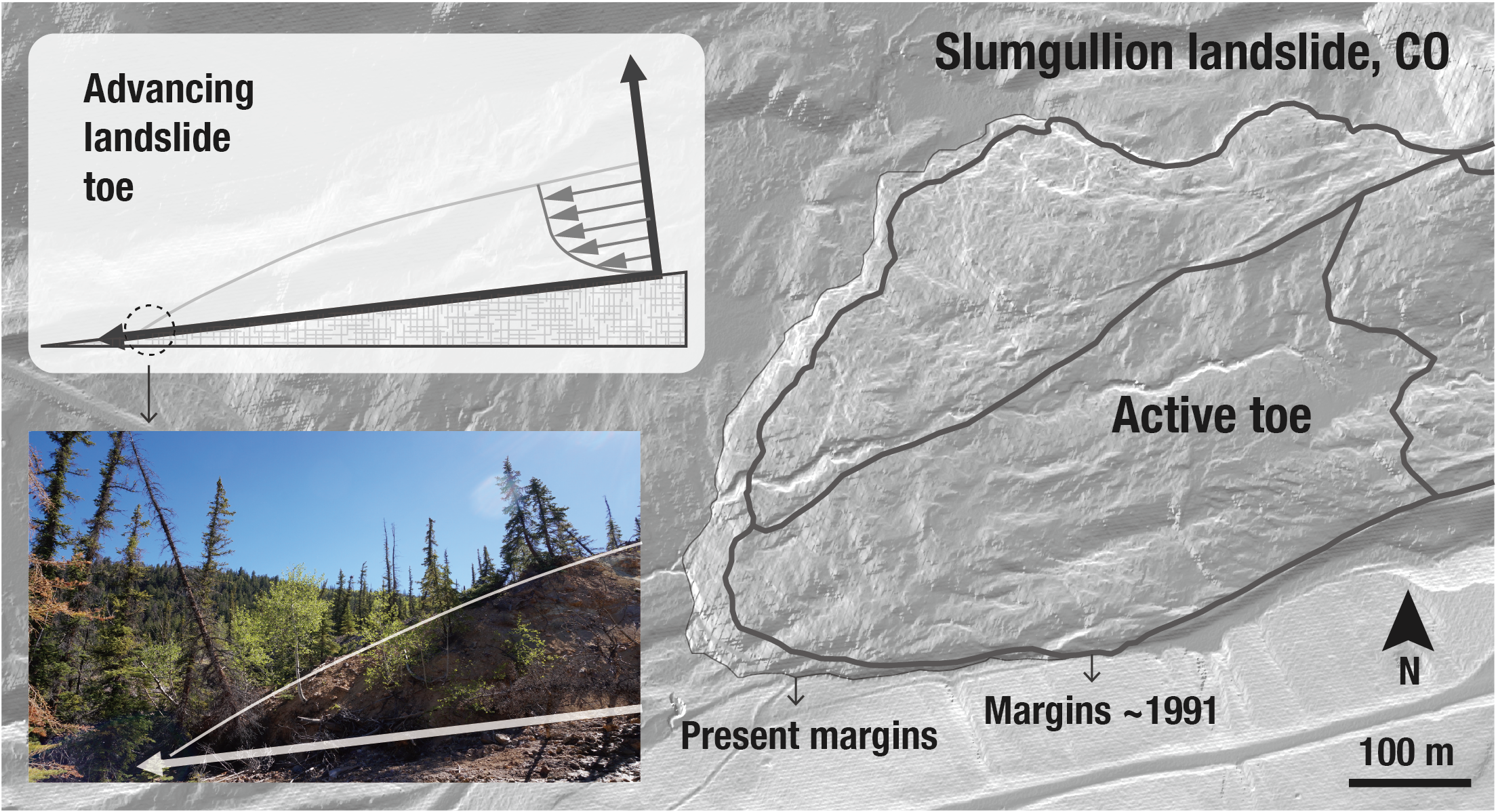
|
8. Rheology of a debris slide from the joint analysis of UAVSAR and LiDAR data
|
2019
|
7. Mobility, thickness, and hydraulic diffusivity of the slow-moving Monroe landslide in California revealed by L-band satellite radar interferometry
|
2018
|
6. Characterization of hydrogeological properties in Salt Lake Valley, Utah using InSAR
|
|
5. Combining InSAR and GPS to determine transient movement and thickness of a seasonally active low‐gradient translational landslide
|
Before 2018
|
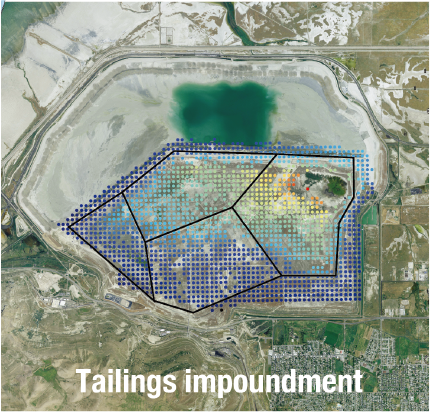
4. Consolidation settlement of Salt Lake County tailings impoundment revealed by time-series InSAR observations from multiple radar satellites
|

|
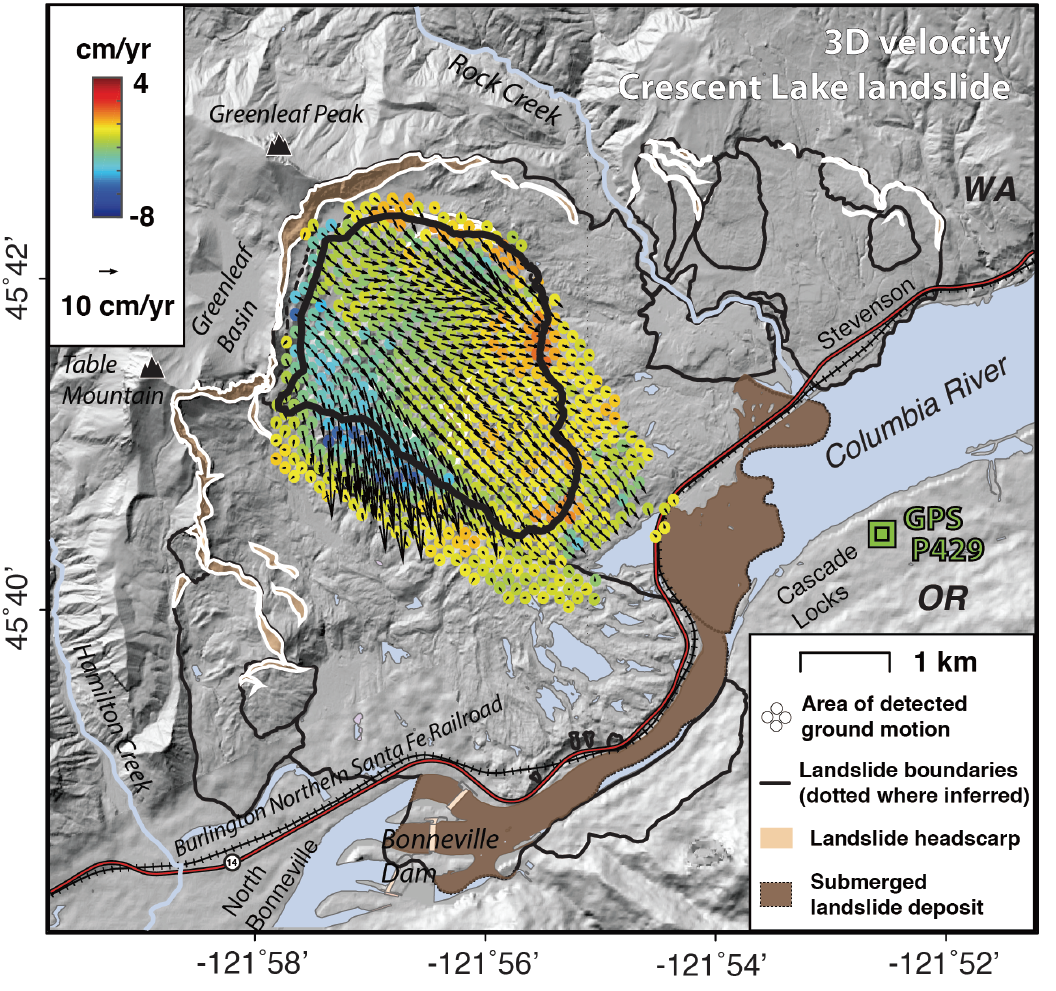
3. Detecting seasonal landslide movement within the Cascade landslide complex (Washington) using time-series SAR imagery
|

|
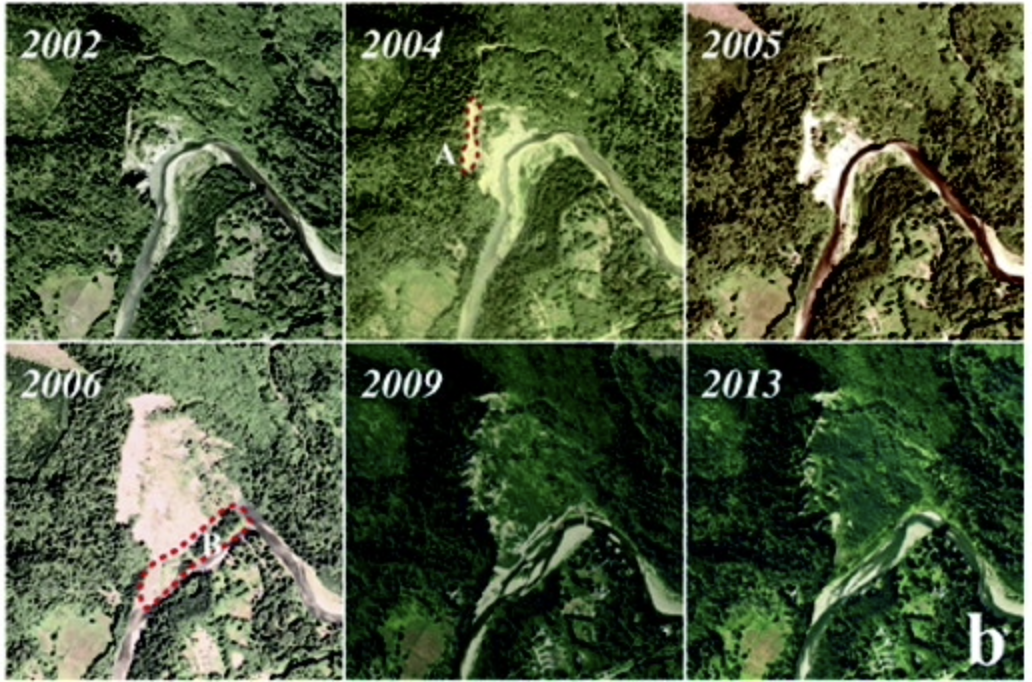
2. Pre-2014 mudslides at Oso revealed by InSAR and multi-source DEM analysis
|
|
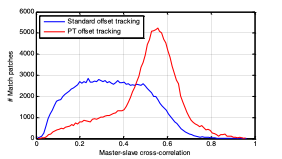
1. Measuring coseismic displacements with point-like targets offset tracking
|